17 Pleural Effusions due to Malignant Lymphoma/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm
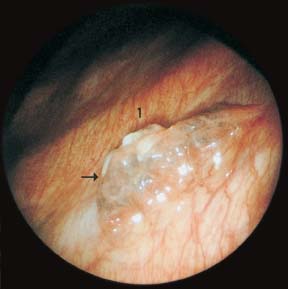
Fig. 17.1
Malignant pleural effusion due to lymphoplasmocytic lymphoma (immunocytoma). After drainage of 2500 mL of cloudy serous effusion: cauliflower-like tumor (→) on the anterior chest wall (1); otherwise normal lung and pleura.
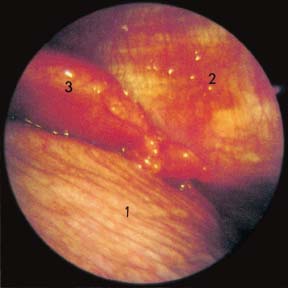
Fig. 17.2
Malignant pleural effusion due to follicular lymphoma. After drainage of 1600 mL of serous effusion: a view of the right costocardiophrenic angle with the diaphragm (1), chest wall (2) injected with many vessels in the parietal pleura, and firm hyperemic fat pad (3) from which a biopsy was taken showing a follicular lymphoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


