in tPA activity (14). Peak tPA levels occur early during CPB within 30 to 60 minutes. Increased soluble fibrin is a powerful stimulator of tPA (12). Unfractionated heparin in itself is also a mild stimulator of vascular plasminogen activators, thereby contributing to fibrinolytic augmentation (20). This hyperfibrinolytic state consumes fibrinogen, thereby impairing coagulation postoperatively. In addition to fibrin, plasmin cleaves fibrinogen and a variety of plasma proteins. The breakdown of fibrin strands by plasmin results in the release of fibrin degradation products that include D-dimers. D-Dimer levels have been used as indicators of fibrinolysis in many studies.
thus potentially lead to increased serum concentrations when TXA is administered by continuous infusion. Various suggestions for reduction in TXA infusion rates in the setting of renal dysfunction are shown in Table 21.2.
TABLE 21.1. Comparison of antifibrinolytic drugs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
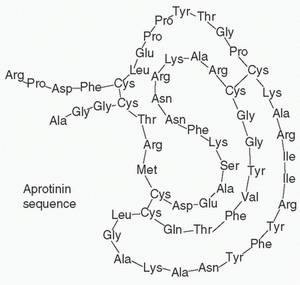
aminocaproic acid, and aprotinin have all been described. For TXA, the dosing regimens have consisted of administration of 1 to 2.5 g in 100 to 250 mL into the pericardial cavity at the time of surgery, either alone or combined with systemic administration. The theoretical advantage of topical administration is targeted local effect with avoidance of any systemic absorption and systemic side effects (37). Some small individual studies have shown a trend toward decreased bleeding and transfusion requirements (38,39,40,41); meta-analysis suggests significant reduction in chest tube losses and transfusion rates (42,43).
TABLE 21.2. Suggested reduction in tranexamic acid maintenance infusion rates in renal disease | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 21.3. Reported dosing regimens for tranexamic during cardiac surgery | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|