Papillary Fibroelastoma
Joseph J. Maleszewski, M.D.
Allen P. Burke, M.D.
Definition and Histogenesis
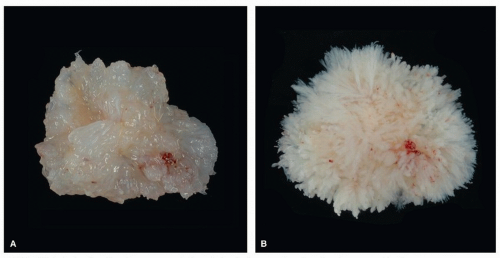
Papillary fibroelastomas are benign endocardial growths that consist of arborizing, avascular, fibroelastotic fronds enveloped by endothelium. Their nature is somewhat unclear, but there is increasing evidence that they represent reactive phenomena, often arising on traumatized or damaged endocardial surfaces.
Incidence
Clinical
Papillary fibroelastoma is somewhat more common in women, with nearly all cases presenting in adults (mean age of ˜60 years).4,5,6,7 Most symptoms arise from left-sided lesions that embolize surface thrombus or the papillary fronds themselves into the cerebral circulation or prolapse into the coronary orifice.8,9,10 The most common manifestations of embolism are transient neurologic defects and myocardial ischemia11,12 and rarely sudden death.13,14,15
There is an association with valvular heart disease, such as rheumatic disease, likely owing to the endocardial injury that such imparts.16 About 20% of papillary fibroelastomas develop as a result of iatrogenic factors,15,17 including thoracic irradiation and open heart surgery (subaortic septal myectomy, valve repair, valve replacement, and repair of congenital defects).15,18,19
Imaging
Papillary fibroelastomas are often first visualized by two-dimensional echocardiography, and the tumor may be an incidental finding or be detected after cerebral ischemia.20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27 They usually arise singly, but multiple lesions are found in between 10% and 30% of cases.28 The added resolution of transesophageal echocardiography is helpful in cases of those papillary fibroelastomas that arise in unusual sites, such as nonvalvular surfaces.29,30
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree