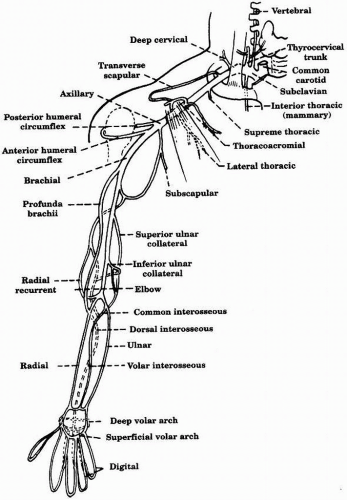
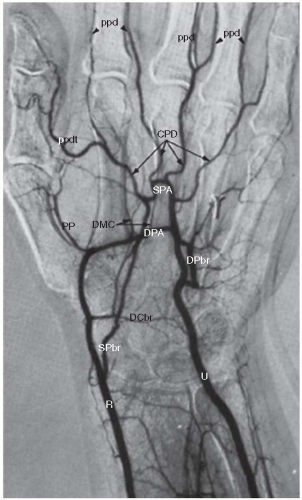
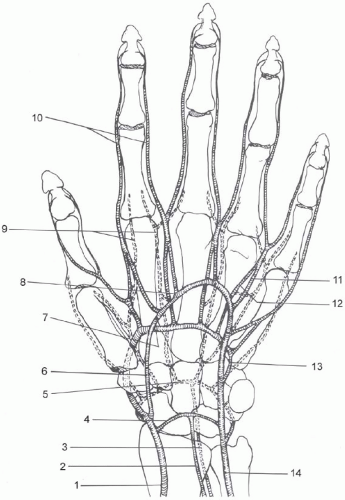
duplicate arteries can potentially decrease the sensitivity of noninvasive testing (pressure measurements and plethysmographic waveforms) in identifying UEAD. For example, normal forearm and digital pressures as well as pulsed volume recording (PVR) waveforms may be obtained in the setting of an occluded ulnar artery.
TABLE 16.1 CLASSIFICATION SCHEME FOR UPPER EXTREMITY ARTERIAL DISEASE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
digital perfusion intermittently ceases. Physiological vasospasm is never associated with complete cessation of digital perfusion. Primary Raynaud’s syndrome only involves functional alterations, whereas secondary Raynaud’s syndrome also involves associated structural microvascular abnormalities. The pathogenesis of Raynaud’s syndrome includes defects in one of more of these three systems: (a) vascular (endothelial dysfunction; structural defects), (b) neural (central dysfunction; impaired vasodilation; impaired vasoconstriction), and (c) intravascular abnormality (increased platelet activation and aggregation; impaired fibrinolysis).
TABLE 16.2 ARTERIAL VARIANTS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||