Purpose
Cardioneuroablation (CNA) is a little known technique for management of patients with excessive vagal activation, based on radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) of autonomic connections in the three main ganglia around the heart. We hypothesized that RFCA of these selected ganglia via right (RA) and/or left atrium (LA) can lead to parasympathetic denervation.
Methods-Results
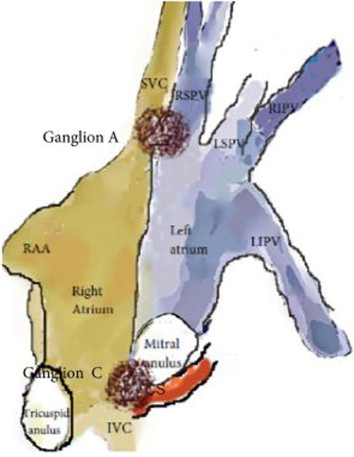
Fourteen patients with mean age of 40±17 years, presenting symptomatic functional bradyarrhythmias and syncope, diagnosed with neurally mediated reflex syncope (NMS), symptomatic atrioventricular (AV) block and symptomatic sinus node dysfunction (SND) (n=6;4;4, respectively) were enrolled. Anatomical mapping of RA and LA were performed with electro-anatomical mapping system. Neuro-myocardial interfaces which present a heterogeneous and coarse segmented spectrum and identified by high-frequency stimulation used as ablation target and ablated until atrial electrical potential was completely eliminated (<0.1mV).
The patients with NMS were free from new syncopal episode at 6 months follow-up after the staged procedure through LA and RA. RFCA via only RA demonstrated success with relief of symptoms in three of four patients with AV block. Despite the increased heart rate, the resolution of AV block after the RFCA could not be achieved in one patient who had partially resolution with atropine infusion on admission. In all patients with SND, resting heart rate was significantly increased after ablation via both atria and maintained at 6 months follow-up.
Methods-Results
Fourteen patients with mean age of 40±17 years, presenting symptomatic functional bradyarrhythmias and syncope, diagnosed with neurally mediated reflex syncope (NMS), symptomatic atrioventricular (AV) block and symptomatic sinus node dysfunction (SND) (n=6;4;4, respectively) were enrolled. Anatomical mapping of RA and LA were performed with electro-anatomical mapping system. Neuro-myocardial interfaces which present a heterogeneous and coarse segmented spectrum and identified by high-frequency stimulation used as ablation target and ablated until atrial electrical potential was completely eliminated (<0.1mV).
The patients with NMS were free from new syncopal episode at 6 months follow-up after the staged procedure through LA and RA. RFCA via only RA demonstrated success with relief of symptoms in three of four patients with AV block. Despite the increased heart rate, the resolution of AV block after the RFCA could not be achieved in one patient who had partially resolution with atropine infusion on admission. In all patients with SND, resting heart rate was significantly increased after ablation via both atria and maintained at 6 months follow-up.
Conclusion
CNA may be an alternative and safe strategy to reduce NMS episodes, and to treat functional AV block and symptomatic SND especially in young patient.
| PIN | Diagnosis | Age | PreA BCL (ms) | Post-LAA* BCL (ms) | Post-RAA** BCL (ms) | PreA WP (ms) | Post-LAA* WP (ms) | Post-RAA** WP (ms) | PreA CSNRT | Post-LAA* CSNRT | Post-RAA** CSNRT | TEP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NMS | 50 | 1404 | 804 | 649 | 280 | 260 | 180 | 42 | |||
| 2 | NMS | 18 | 1152 | 928 | 751 | 310 | 280 | 190 | 32 | |||
| 3 | NMS | 34 | 1226 | 815 | 694 | 330 | 290 | 210 | 36 | |||
| 4 | NMS | 38 | 1250 | 876 | 784 | 370 | 310 | 220 | 34 | |||
| 12 | NMS | 21 | 1376 | 916 | 704 | 320 | 290 | 190 | 33 | |||
| 13 | NMS | 19 | 1378 | 861 | 802 | 300 | 280 | 210 | 39 | |||
| 7 | SND | 70 | 1440 | 875 | 724 | 620 | 440 | 410 | 35 | |||
| 8 | SND | 34 | 1350 | 854 | 708 | 570 | 485 | 430 | 37 | |||
| 9 | SND | 36 | 1276 | 825 | 704 | 565 | 410 | 380 | 35 | |||
| 14 | SND | 28 | 1268 | 811 | 716 | 550 | 380 | 360 | 32 |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


