Miscellaneous Lesions
Pericardial Disease
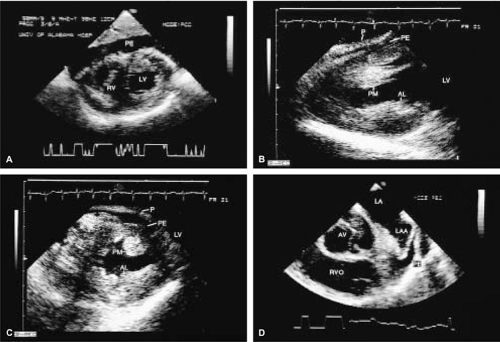
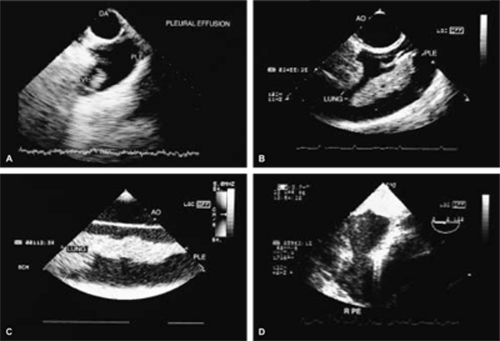
A small amount of pericardial fluid is normally present between the visceral and parietal pericardium (approximately 20 to 30 mL). Larger collections present as an echo-free space. While three-dimensional echocardiography, or computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) permit precise quantification of the amount of pericardial fluid, such numbers are seldom, if ever, used. Hence, a semiquantitative approach is used. A pericardial effusion is regarded as small when the maximum width is <10 mm, moderate when the maximum width is between 10 mm and 15 or 20 mm and large beyond that. In addition to the size, the rate at which the effusion accumulates determines its physiologic significance. Slower accumulation allows a gradual increase in the compliance of the pericardium, sometimes allowing massive effusions to form without tamponade. Diastolic collapse of the right atrium and/or right ventricle suggests cardiac tamponade; the latter is more specific than the former.
When both a pleural and a pericardial effusion are present, the width of the pericardium can often be measured, a point in the differential diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis (constrictive pericarditis generally causes thickening of the pericardium to >5 mm).
Most often, pericardial effusions can be adequately worked up with transthoracic echocardiography but the same information is available through transesophageal echocardiography.
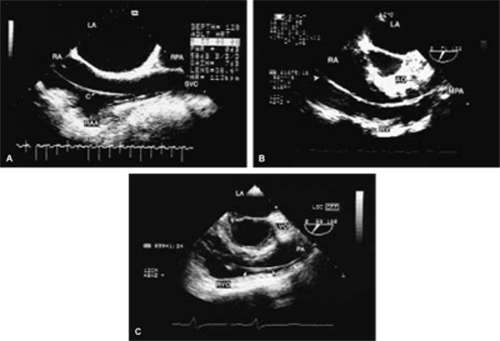
Pericardial cysts are benign collections of fluid that abut and distort the border of the heart. Color flow Doppler can be used to rule out fluid flow within the structure. MRI and CT can confirm the diagnosis and provide an insight regarding the anatomic topography of the cyst.
Other Miscellaneous Lesions
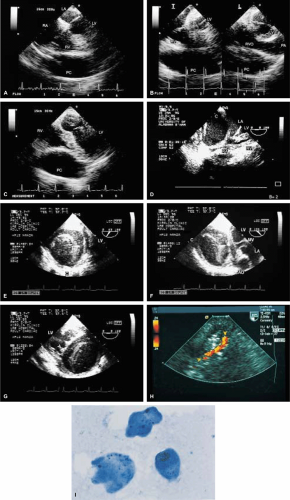
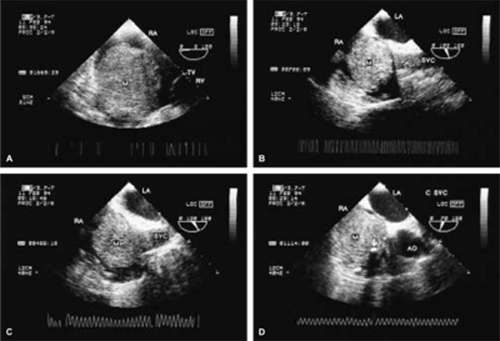
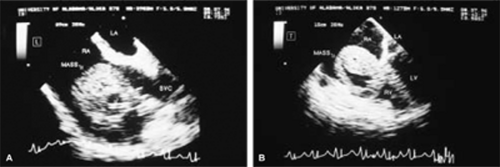
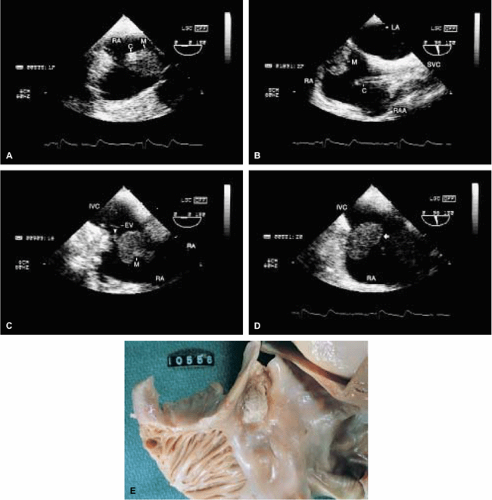
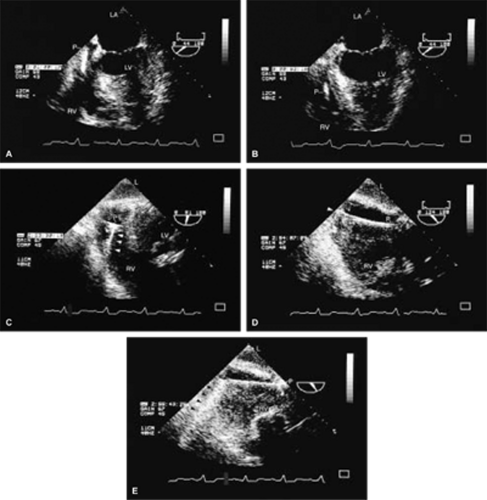
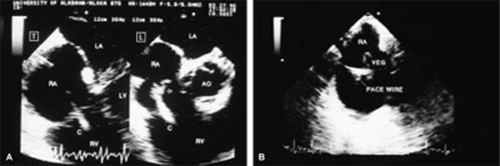
Examples of a variety of other lesions including pleural effusion, right heart catheters with associated thrombus, pacemaker wires, pacemaker vegetations, artifacts, contrast effects during cardiac surgery, left ventricular assist devices, and intraaortic balloon pumps are shown in this chapter.