Fig. 20.1
The three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis creates a firmer erection than its two-piece counterpart. This fluid-filled implant features two inflatable cylinders implanted in the penis, a pump placed in the scrotum, and a reservoir implanted in the lower abdomen. When you are ready to have sex, you pump the fluid from the reservoir into the cylinders to create a rigid erection. After sexual intercourse, you release the valve inside of the scrotum to drain the fluid back into the reservoir to return to flaccidity
Mentor manufacturers two to three-piece inflatable prostheses: the Alpha I and the Alpha I Narrow Back, a small-diameter version for men with fibrotic penises [17].
Nowadays in extended use is the AMS INIBHIZONE already embedded in antibiotic (solution) and the COLOPLAST TITAN OTR embedded in antibiotic solution during the surgical procedure.
20.3.3 Preparing to the Surgery
The patient must be prepared for the surgery to decrease the risk of infections. Some general rules are to start scrubbing the external genitalia with povidone solution a week before the procedure. Some authors suggest to sterilize the urine with ofloxacin 5 days before the surgery. The standard procedure is the combination of gentamycin (80 mg tid) and vancomycin (1 g bid) starting the day of the surgery and for 2 days after.
Some authors are used to irrigate the surgery field with a solution of vancomycin (2 g) and protamine that allows the antibiotics to enter through the bacterial shields [18].
20.3.4 Surgical Approaches
The Infrapubic Approach
This approach that consists of a small vertical or transverse incision is made below the pubis just above the penis. The main advantage of this method is the possibility to place the reservoir under direct vision. Disadvantages: limit of corporeal exposure, impossibility to anchor the pump in the scrotum, and possible damage to the dorsal nerves of the penis.
The Penoscrotal Approach
The penoscrotal approach can be made through a vertical midline incision over the urethra at the penoscrotal junction or through a transverse scrotal incision about 1 cm below the penoscrotal junction. In both techniques dartos fascia is incised in line with the incision, exposing the midline urethra and the corpora or either side. The surgeons prefer the transverse scrotal approach because retraction on the transverse lower flap of the dartos fascia exposes both crura nearly to the pelvic bone attachments. If further distal exposure is needed, the incision can be extended in an inverted T-fashion to the frenular area. To the surgeons’ knowledge, this approach is the only incision that can almost completely expose both corpora. The penoscrotal approach also permits to fix the pump in its subdartos pouch by passing the pump tubes through three separate stab incisions in the back wall of the pouch. The main advantage of the penoscrotal approach is that it avoids possible damage to the dorsal penile nerves. The disadvantage is that it needs blind placement of the reservoir [17].
20.3.5 Infection
When using silicone, our body forms a fibrous pseudocapsule around it. When infections arise in the space between this capsule and the prosthesis (periprosthetic infections), the device must be removed. Most infections are the result of the implant procedure; however, infections may occur many years after their implantation because of blood-borne organisms from distant infections. Infections are more frequent in secondary implants or procedures associated with reconstruction. Jarow reported a 1.8 % infection rate in 114 primary procedures, a 13.3 % infection rate in 30 secondary procedures, and a 21.7 % infection rate in 23 implants connected with reconstructive procedures.
It is not clear whether diabetes increases the risk for periprosthetic infection. In a study a higher risk was proved in diabetics with glucosylated hemoglobin around 11.5 %. In another study no correlation was found between infections and glucosylated hemoglobin. In two other studies there were no significant differences between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.
When a periprosthetic infection occurs, it is necessary to remove the entire prosthesis because there are bacteria in a biofilm that is adherent to the device. For many years, the reimplantation of the device was delayed for 6–12 months. Infection destroys some or all of the corpora cavernosa, and a scar occurs. With time, this scar contracts and the penis becomes smaller and creates difficulties in placing the cylinder during the implantation.
20.3.6 Mechanical Reliability and Patient Satisfaction
In a long-term (median follow-up 47.7 months) multicenter study made in the United States, AMS 700CX inflatable prosthesis was evaluated for longevity, morbidity, and patient satisfaction rates. The control was carried out in two phases. Phase 1 was a medical record review of 372 patients who had implantation with the AMS 700CX penile prosthesis from 1987 to 1996 by seven frequent penile prosthesis implanters. Phase 2 was a telephone interview of 207 men by a neutral observer. For the 372 men in phase 1, mean device mechanical reliability was 92.1 ± 3.3 % after 3 years and 86.2 ± 4.6 % after 5 years. 3.2 and 17.5 % of the cases, respectively, developed postoperative infection and device malfunction. In phase 2, of the 207 patients called, 86.2 % still had an AMS 700CX penile prosthesis implanted and 87.1 % with erection suitable for coitus; 88.2 % would suggest an implant to a relative or a friend [20, 21].
20.4 Low-Intensity Shock Wave Therapy
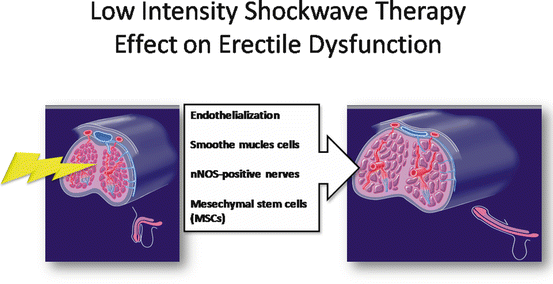
The most recent treatment for ED is the shock wave therapy for the revascularization of the corpus cavernosum in cases of vascular ED [22]. The treatment can be done using either electrohydraulic or electromagnetic sources of producing shock waves. In the first animal study, the researchers demonstrated that low-intensity shock wave therapy (Li-SWT) promotes regeneration of nNOS-positive penile dorsal nerve, penile dorsal artery, and penile sinusoids [23]. Tom Lue’s team also found out that Li-SWT promotes the re-endothelialization of the penile sinusoids and arteries and penile smooth muscle content [24]. These beneficial effects are possibly mediated by increased recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that promote the regeneration of diabetes mellitus-damaged erectile tissues (Fig. 20.2). This group demonstrated upregulation of the expression of α-SMA, vWF, nNOS, and VEGF. They also demonstrated that the therapeutic effect might relate to the treatment dose positively and the maximal therapeutic effect was achieved in Li-SWT of 300 shocks per treatment site and energy of 7.33 MPa [25]. After that, they decided to apply this animal model to human corpora cavernosum. The first double-blinded placebo control showed that 68 % of the patients went from Erection Hardness Score (EHS) 1 and 2 to EHS 3 and 4 involving patients responding to PDE5 Inhibitors. Another study demonstrated that the patients at baseline did not respond to PDE5 inhibitors but with the shock waves treatment, they regained their ability to respond to PDE5 inhibitors and to have sex life. It is possible that with further treatments, these patients will not require PDE5 inhibitors [25]. Also 6 months after the treatment, a significant number of patients maintain their good result [26, 27] (Fig. 20.3).
 < div class='tao-gold-member'>
< div class='tao-gold-member'>





Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


