CHAPTER 16 Left Upper Lobe Apical Trisegmentectomy—Video 16-1
 Video-Assisted Left Upper Lobe Apical Trisegmentectomy
Video-Assisted Left Upper Lobe Apical Trisegmentectomy
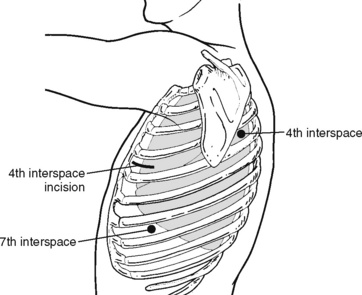
Step 1. Port Placement (Figure 16-1)
♦ Place the camera port in the seventh intercostal space in the anterior axillary line; it can be modified depending on heart size.
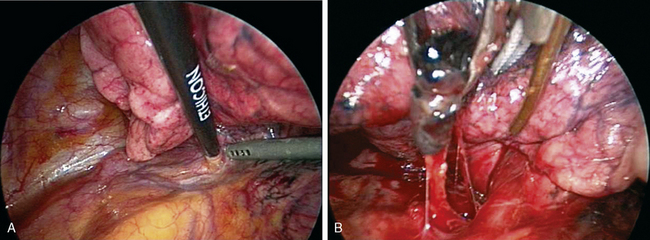
Step 2. Dissect Anterior Hilum and Aortopulmonary Window (Figure 16-2)
♦ Place the thoracoscope in the camera port with the side arm to the left to look at anterior hilar structures.
♦ Open the mediastinal pleura over the anterior hilum with an endokittner and the suction irrigator. This defines the venous drainage from the upper division of the left upper lobe (LUL). Dissect superiorly to the level of the aortopulmonary window.
♦ Removal of the level 5 nodes facilitates exposure of the vessels and prepares the superior and posterior aspect of the anterior trunk for subsequent transection.
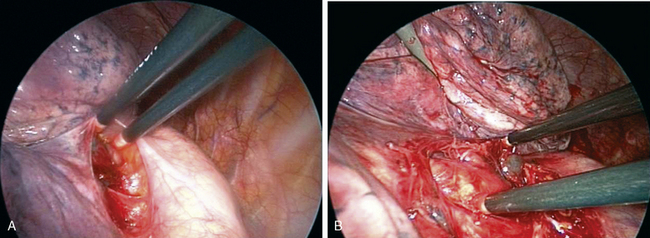
Step 3. Open Posterior Mediastinal Pleura (Figure 16-3)
♦ Open the posterior mediastinal pleura using blunt dissection with endokittners through the posterior port. Continue opening the pleural superiorly until the dissection connects with the posterior pleural opening with the anterior pleural dissection from steps 1 and 2.
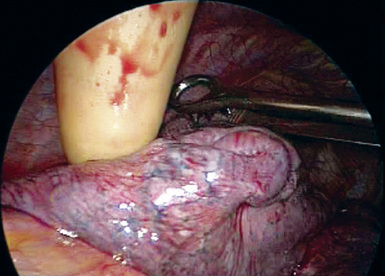
Step 4. Tumor Palpation (Figure 16-4)
♦ Exposure: Move the lung toward the access port with a ringed forceps placed through the posterior port.
♦ Carefully palpate and examine the tumor to be certain a sublobar resection constitutes optimal cancer treatment. This is done by corroborating the tumor size (T1, ideally less than 2 cm) and confirming that tumor is far enough away from the lingula so that the margins will be adequate if a trisegmentectomy is performed.
♦ When observing the LUL from an anterior position, the lingular vein helps to determine the superior aspect of the lingula. When retracting the LUL posteriorly, the upper division is just above the lingular vein. There is often a minimal fissure between the lingula and the upper division.
Step 5. Upper Pulmonary Vein (Figure 16-5)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree