Section 6 Ischaemic heart disease
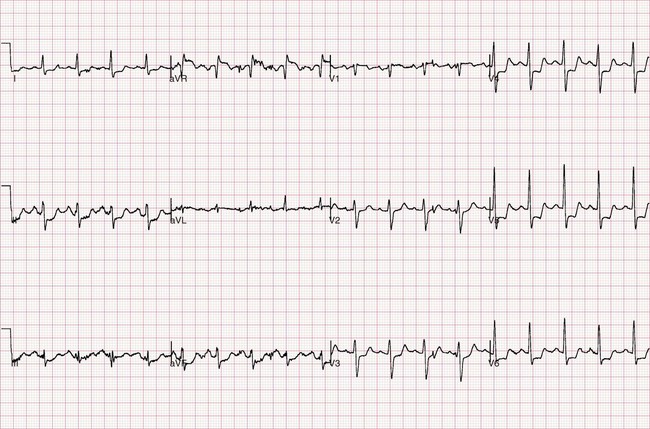
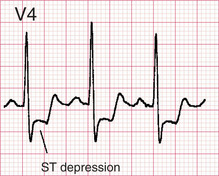
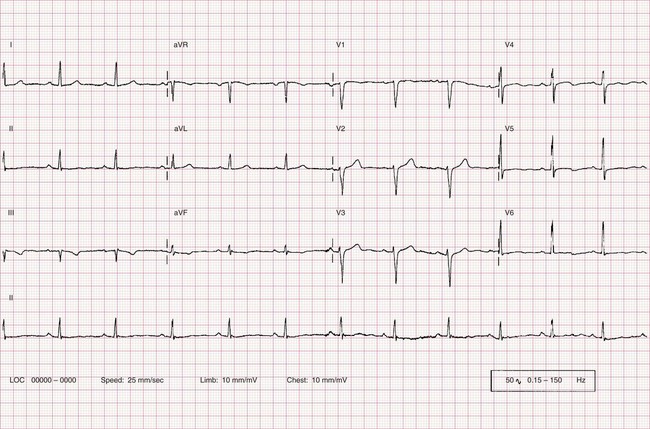
Myocardial ischaemia – ST depression
Horizontal ST depression is strongly suggestive of ischaemia in an appropriate clinical setting. Sloping ST depression is a less reliable indicator of ischaemia.
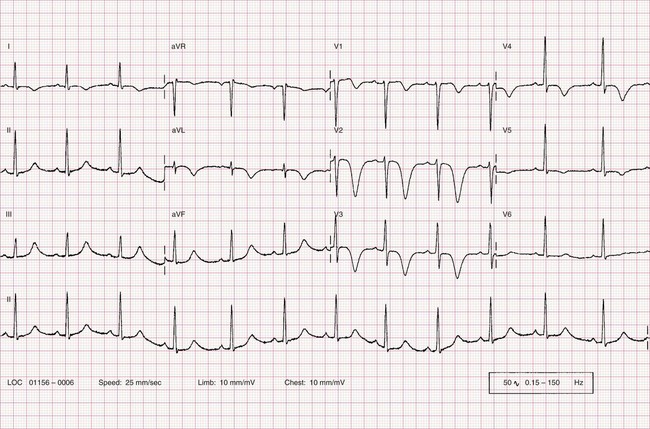
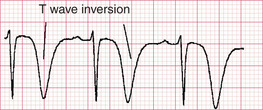
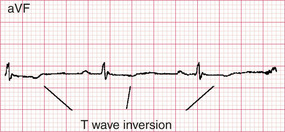
Myocardial ischaemia – T wave inversion
There are no definitive criteria for the normal T wave and numerous conditions other than ischaemia can cause T wave changes (see CASE 58). Inversion of the T wave is considered abnormal in V3-6, I, II and aVF in most adults. T wave inversion is relatively non-specific for ischaemia unless it is deep and symmetrical (‘arrowhead’) inversion.
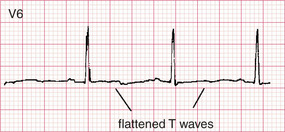
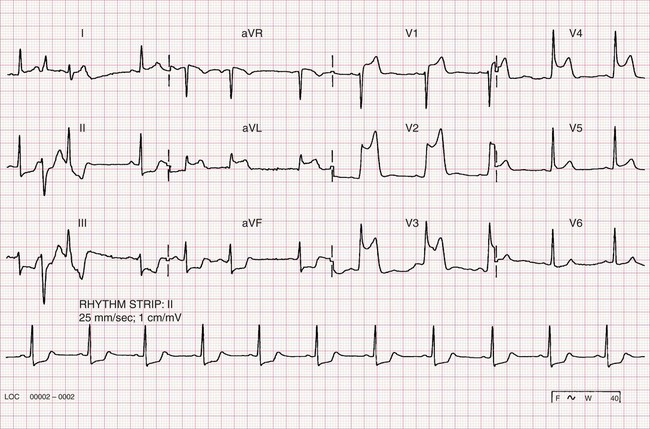
Myocardial ischaemia – non-specific changes
Usually the ECG changes of ischaemia are more subtle than those shown in the previous two examples and are referred to as non-specific ST and T wave changes. These changes include minimal or sloping ST depression, T wave flattening, abnormally tall T waves, and minimal T wave inversion.