Fig. 46.1
Coronary rotational ablation in Kawasaki disease. (a) Before the intervention, (b) rotational ablation, and (c) post-rotational ablation. Coronary stenosis is completely resolved
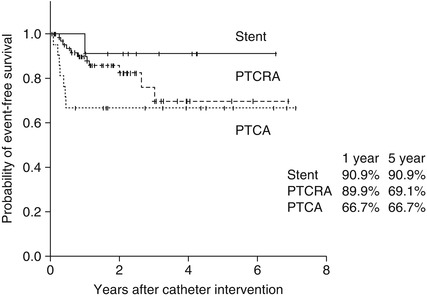
Fig. 46.2
Long-term outcome after catheter intervention in Kawasaki disease (PTCA percutaneous coronary angioplasty, PTCRA percutaneous coronary rotational ablation)
Anticoagulation and antiplatelet medication should be continued through their life. Intravascular ultrasound imaging provides valuable information for the selection of the appropriate interventional procedure and early detection of vascular complications.
46.3.3 Other Special Conditions
46.3.3.1 Tetralogy of Fallot
The most frequent abnormality seen in coronary artery branching in tetralogy of Fallot is the presence of a coronary artery crossing the right ventricular outflow tract. This can be a left anterior descending coronary artery from the right coronary artery with an anterior course.
46.3.3.2 Post-arterial Switch Evaluation
First of all, it is mandatory to know the spectrum of coronary artery variations seen in d-TGA (Fig. 46.3) and the surgical report.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>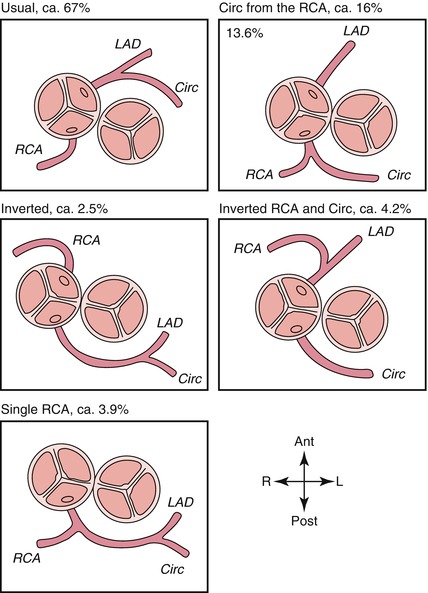 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


