We describe a 45-year old man who experienced a potentially fatal arrhythmia after consumption of multiple energy drinks. At 5 years old, he underwent “repair” of tetralogy of Fallot using a patch in the right ventricular outflow tract, and at age 40 had an automatic implantable cardiac defibrillator (AICD) placed. His first AICD shock occurred within 30 minutes after he finished the third energy drink and was preceded by feelings of lightheadedness and severe dizziness. Without the AICD, he likely would have died. The risk of consuming energy drinks in those with underlying structural heart disease and the general population should be determined. Warning labels should be required to inform consumers of the risks posed by these drinks and of appropriate limits for consumption.
Highlights
- •
Sudden cardiac death was aborted in a 45-year-old man with tetralogy of Fallot repaired during childhood, with implantable cardiac defibrillator firing after 3 energy drinks.
- •
Energy drinks increase risk for ventricular arrhythmias in at-risk populations.
- •
At-risk populations include those with underlying structural heart disease.
- •
Energy drink safety is not established, especially for at-risk populations.
Energy drinks are a growing industry selling multiple billions of dollars of product each year. These drinks contain large amounts of caffeine, as well as various caffeine-containing herbal supplements, including taurine and guarana ( Table 1 ). Alone and combined, at high doses, these ingredients can cause arrhythmias, especially in patients with structural heart disease. We describe a potentially fatal arrhythmia after consumption of multiple energy drinks.
| Drink | Amount of Caffeine (mg) | Amount of Sugar (g) | Amount of Taurine (mg) | Active Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Bull 8.3 oz | 83 | 27 | 1000 | L-carnitine, glucose, caffeine, guarana, inositol, glucuronolactone, maltodextrin |
| Monster 8.0 oz | 92 | 27 | 1000 | Glucose, caffeine, guarana, L-carnitine, inositol |
| Rockstar 8.0 oz | 229 | 0 | 1000 | Taurine, ginkgo, guarana, caffeine, inositol, L-carnitine |
| Amp 8.0 oz | 71 | 29 | 14.2 | Guarana, caffeine, ginseng, taurine |
| Verve 8.3 oz | 80 | 18 | 1000 | Taurine, inositol, D-ribose, choline chloride |
| 5-Hour energy 2.0 oz | 215 | 0 | Not documented | Taurine, glucuronic acid, malic acid, caffeine, N-acetyl L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine |
Case Description
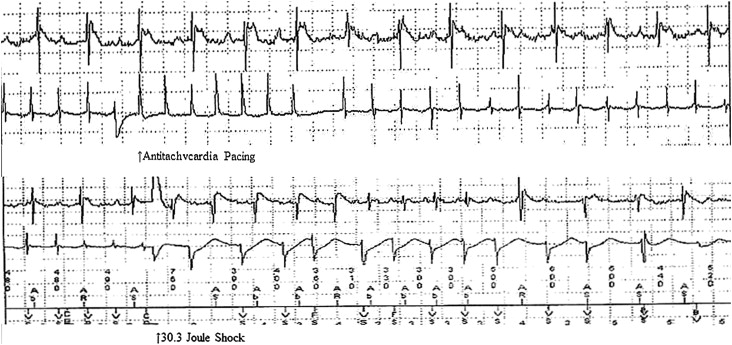
A 45-year-old man who underwent “repair” of tetralogy of Fallot at the age of 5 years using a patch in the right ventricular outflow tract and had an automatic implantable cardiac defibrillator (AICD) placed at the age of 40 years reported to his cardiologist because of his first AICD shock. He had been hospitalized several times previously for heart failure. His left ventricular ejection fraction was approximately 25%. He awoke tired for an early workday and over 3 to 4 hours consumed 3 Red Bull energy drinks. The AICD shock occurred within 30 minutes after he finished the third drink and was preceded by feelings of lightheadedness and severe dizziness. Device interrogation revealed nonsustained ventricular tachycardia and several rounds of antitachycardia pacing at the onset of ventricular tachycardia, then a 30-J defibrillator shock for ventricular fibrillation ( Figure 1 ). Previous device interrogations had shown nonsustained ventricular tachycardia but none requiring device intervention.