2 Echocardiographic Assessment of Patients with Systolic Heart Failure
Definition, Staging, and Etiology of Systolic Heart Failure
• Heart failure (HF): abnormality of cardiac function responsible for inability of the heart to provide blood flow at rates commensurate with tissue requirement, or to do so only at increased filling pressures.
• The single most useful diagnostic test in the evaluation of patients with HF is the comprehensive two-dimensional (2D) echocardiogram coupled with Doppler flow studies.1 The goals of echocardiography in systolic HF are:
• Define etiology and in particular determine if systolic HF is due to a primary myocardial disease (including consequences of coronary disease) or a primary valve disease.
• Define the presence and severity of functional mitral regurgitation (MR) and/or tricuspid regurgitation.
TABLE 2-1 LEFT VENTRICULAR QUANTIFICATION METHODS: USE, ADVANTAGES, AND LIMITATIONS
| Dimension/Volumes | Use/Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | ||
| M-mode | Reproducible | Beam frequently off-axis |
| High frame rates | Single dimension not representative in distorted ventricles | |
| 2D-guided | Assures orientation perpendicular to LV axis | Lower frame rates than in M-mode |
| Single dimension only | ||
| Volumetric | ||
| Biplane Simpson’s method | Corrects for shape distortions | Apex frequently foreshortened |
| Minimizes mathematic assumptions | Endocardial dropout | |
| Relies on only two planes | ||
| Area-length method | Partial correction for shape distortion | Based on mathematic assumptions |
| 3D echocardiography | Best correlation with MRI | Endocardial definition |
| Further enhanced by contrast use | ||
Echocardiographic Methods for Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Image Acquisition and Interpretation
• Various imaging modalities can be used for assessment of left ventricular systolic function (see Table 2-1).
• Image optimization is a key step in obtaining accurate measurements. Always adjust focus depth, sector size, and lateral gains to optimize axial and temporal resolution.
Indexes of Global Left Ventricular Systolic Function
• Left ventricular size
• LV size is measured by the diameter at the mitral leaflet tips; calculation is simple but not linearly related to LV volumes.
• EF by visual assessment
• This value is an estimation based on appreciation of ventricular area change in systole from multiple views.
• Calculation is simple but underestimates EF in the very low range (an area change of 10% equals an EF of 19%).
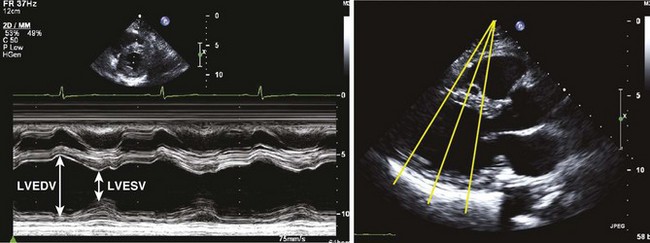
• EF by linear measurements (Figure 2-1)
• Electrocardiography (ECG) serves only as a guidance; valve and wall motion should also be considered in selecting end-diastolic and end-systolic frames.3
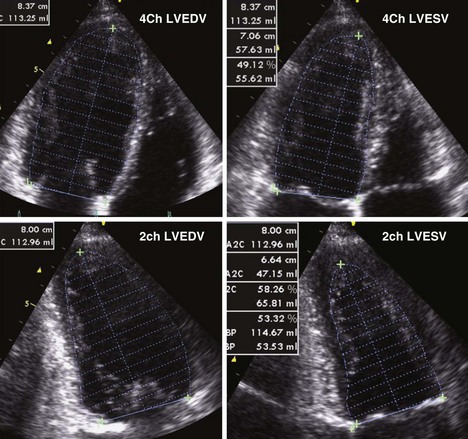
• EF by volumetric measurements (Figure 2-2)
• LV apical foreshortening and lateral resolution on 2D images can be significant limitations (see Table 2-1).
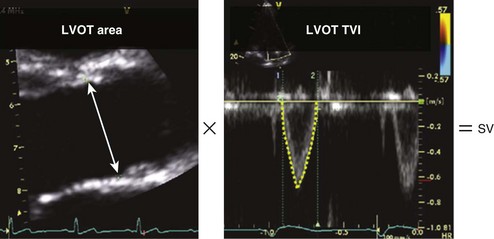
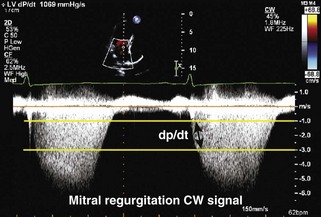
• Stroke volume and cardiac output (Figure 2-3)
• These values are based on 2D (LV outflow tract [LVOT] dimension and calculated area) and Doppler (blood velocity) measurements, with calculation of stroke volume as the product of LVOT area by time-velocity integral (TVI).
Assessment of Regional Left Ventricular Function
• RWMA due to ischemia does not occur at rest until epicardial coronary artery stenosis is greater than 85%.
• Echocardiography overestimates the area of ischemic or infarcted myocardium as adjacent regions are affected by tethering, regional loading conditions, and stunning.
• The presence of regional left ventricular dysfunction not respecting coronary distribution can be seen in various diseases, such as post–coronary artery bypass grafting, infiltrative cardiomyopathies (sarcoidosis), cardiac tumors, myocarditis, etc.
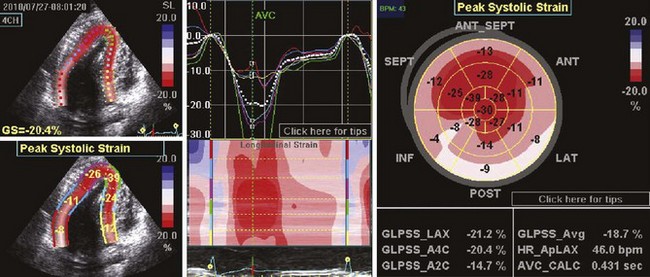
• Other tools are gaining momentum in assessing regional wall motion, particularly segmental left ventricular strain or strain rate (see Figure 2-4).
Assessment of LV Diastolic Function
• Diastolic dysfunction analysis is based on the combination of mitral and pulmonary venous flows and TDI.
Assessment of Hemodynamic Consequences
• Estimate right atrial pressure using inferior vena cava size and variation, and right ventricular pressure using tricuspid regurgitation velocity.
Key Points
• Left ventricular internal diameter and EF are key parameters in the diagnosis and follow-up assessment of systolic dysfunction.
• The ASE recommends use of biplane method of disks (modified Simpson’s method) for EF calculations.
• Erroneous LVOT measurements can introduce large errors in estimation of cardiac output and severity of valvular disease.
Echocardiographic Assessment of Specific Causes of Systolic Heart Failure
Ischemic LV Dysfunction
• The presence of resting RWMAs in a coronary artery distribution pattern and/or evidence of old myocardial infarction (thinned, scarred myocardial wall; LV aneurysm) are key echocardiographic findings.
• Resting RWMAs can also be seen with stunned/hibernating myocardium and occasionally in non-ischemic disease.
• Intravenous contrast should be used whenever endocardial border definition is suboptimal in two or more contiguous segments.
• Stress echocardiography is an established method of assessment of myocardial ischemia.
• Exercise (treadmill or stationary bike) is the preferred stress method. It can be combined with oxygen consumption for better quantification of exercise ability. Dobutamine is the most commonly used pharmacologic stress agent.
• Interpretation is based on regional wall motion analysis and global response to stress (change in left ventricular dimension and EF with stress).
• MR can be associated with ischemic left ventricular dysfunction, and is most commonly due to tethering of the posterior mitral leaflet (Figure 2-7); an effective regurgitant orifice (ERO) greater than 0.20 cm2 and a regurgitant volume greater than 30 mL are associated with poor prognosis.
• Always assess for intraventricular thrombus in patients with low EF and aneurysmal changes (Figure 2-8). This is best done by administration of intravenous contrast.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree