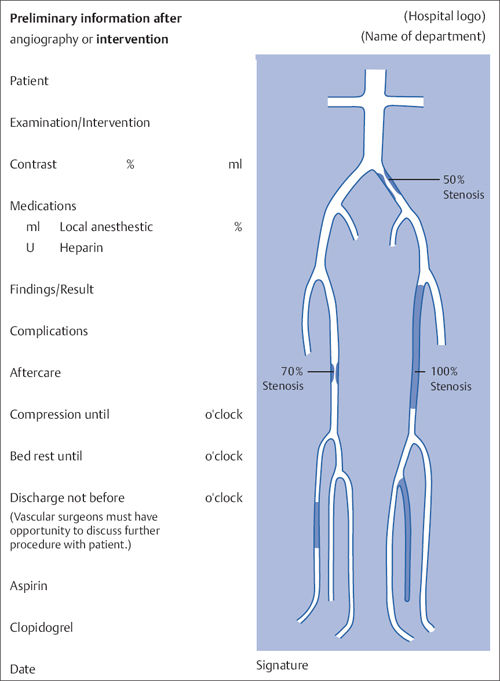
10 Documentation and Postprocessing Once the patient is back in bed after the intervention and the access site has been treated, evaluate the angiographic documentation (Table 10.1): Select the most important images, perform the necessary postprocessing (contrast adjustment, sharpness, and definitive measurement of stenosis grades, see below), and compile a preliminary report for the ward: • Mark the findings and treatment results in a schematic diagram of the vascular tree (Fig. 10.1). • Give preliminary evaluation of treatment results. • List type and quantity of contrast agent. • List type of treatment of vascular access site. • List other aftercare (bed rest). For this purpose, copy the diagram of the vascular tree shown in Fig. 10.3. Paste the name of the department over the top right-hand corner. Paste the name of the preparation used over “Local anesthetic.” Then copy the diagram. Visit every inpatient on afternoon rounds. Check the access site and the results of treatment. Discuss the results and any additional measures with the patient. Some operators delegate the task of postprocessing images to coworkers. Even if they are very good at this, it is not the best solution because certain details are only visualized during postprocessing with optimized window settings and contrast enhancement. Only you can really decide how much of this is important and should be documented. Remember that the quality of your images, in terms of both their information content and their aesthetic appeal, will define your own image among your colleagues in allied disciplines! Subtraction very often requires improvement. There will almost always be several pre-contrast images. The one of these that is closest to the first contrast-filled image will be the most suitable mask. Selecting a different image as a mask has an advantage over pixel shift in that it compensates for even complex motions. Only when one brings together the most suitable mask with the most high-contrast filling image may one start the pixel shift function if necessary. Table 10.1 The physician’s most important tasks after completing the intervention
Image Postprocessing
Image postprocessing |
Preliminary report of findings for the ward |
Visit during afternoon |
Discussion of findings with vascular surgeons |
The rule is that the window setting must be wide enough so that not only the outer contours of the vessel can be evaluated with hard black and white contrast. On the contrary, details within the vessel should be discernible as different gray scale values (Fig. 10.2), and all important details of this sort should be emphasized by contrast enhancement. The angiographic image is only two-dimensional. Information about the third dimension is provided only by the gray scale visualization.
The relationship to bony landmarks is very helpful in many places. What is often missed is visualization of the femoral artery bifurcation and the femoral head on a single image. This can be decisive for selecting the optimal access site in subsequent interventions.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>