1.3 Disorders of gas exchange
Hypoxia, hypoxaemia and impaired oxygenation
The above terms are often used interchangeably but mean different things.
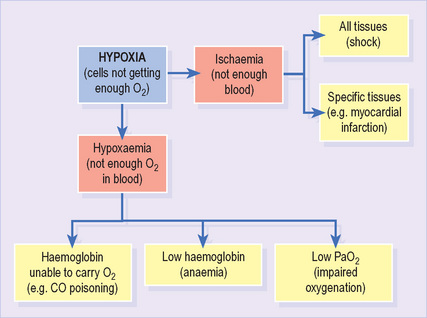
Hypoxia refers to any state in which tissues receive an inadequate supply of O2 to support normal aerobic metabolism1 (Figure 9). It may result from either hypoxaemia (see below) or impaired blood supply to tissues (ischaemia). It is often associated with lactic acidosis as cells resort to anaerobic metabolism.
It is important to note the distinction between impaired oxygenation (which results in hypoxaemia) and inadequate oxygenation (which results in hypoxia). Consider a patient with a PaO2 of 8.5 kPa. He has impaired oxygenation, suggesting the presence of important lung disease. Nevertheless, his PaO2 would usually result in an SaO2 > 90% and, provided the haemoglobin and cardiac output are normal, adequate O2 delivery to tissues.
Type 1 respiratory impairment
Type 1 respiratory impairment1 is defined as low PaO2 with normal or low PaCO2. This implies defective oxygenation despite adequate ventilation. V/Q mismatch is usually responsible and may result from a number of causes (Box 1.3.1). The PaCO2 is often low due to compensatory hyperventilation.
Box 1.3.1 Common causes of type 1 respiratory impairment*
| Pneumonia | Acute asthma |
| Pulmonary embolism | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| Pneumothorax | Fibrosing alveolitis |
| Pulmonary oedema | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
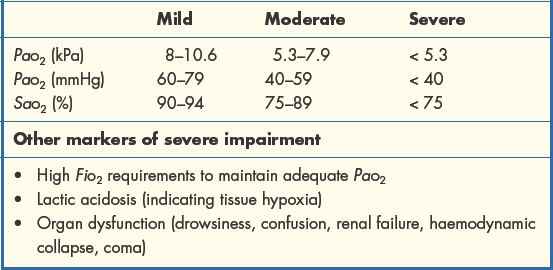
The severity of type 1 respiratory impairment is judged according to the scale of the resulting hypoxaemia and, ultimately, the presence of hypoxia (Table 1.3.1). Here it is important to remember the O2 dissociation curve. Reductions in PaO2 as far as 8 kPa have a relatively minor effect on SaO2 and are well tolerated. Beyond this threshold, we reach the ‘steep part’ of the curve and further reductions in PaO2 will lead to much greater falls in SaO2, significantly lowering the O2 content of arterial blood.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree