Ischemia
Medications
Rheumatologic disease
Infection
Chemotherapeutic agents
Systemic lupus, scleroderma
Virus
Antiretroviral drugs
Endocrinologic disorders
Bacteria
Phenothiazines, chloroquine
Pheochromocytoma, diabetes mellitus
Fungus
Electrolyte abnormalities
Miscellaneous
Parasite
Hypocalcemia, uremia
Radiation
Rickettsia
Hypophosphatemia
Sarcoidosis
Deposition disease
Genetic ± neuromuscular disease
Tachycardia
Hemochromatosis
Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy
Sleep apnea
Amyloidosis
Myotonic dystrophy
Oxygen free radical
Toxins
Friedreich’s ataxia
Autoimmune myocarditis
Ethanol, cocaine
Nutritional deficiencies
Familial cardiomyopathies
Lead, mercury
Thiamine, selenium, carnitine
Peripartum cardiomyopathy
In the World Health Organization classification, DCM is classified as its primary (e.g., idiopathic or familial) and secondary forms.
Up to 50 % of patients diagnosed with idiopathic cardiomyopathy have a familial DCM.
Although genetically heterogeneous, the predominant mode of inheritance for DCM is autosomal dominant, with X-linked autosomal recessive and mitochondrial inheritance less frequently.
13.2 Imaging Modalities and Findings
13.2.1 Computed Tomography
With ECG-gated cardiac CT, coronary artery disease can be excluded because of high specificity and negative predictive value.
Although ionizing radiation and injection of relatively large amounts of iodinated contrast agents are required, ECG-gated CT scanning enables morphological analysis of the ventricles and is an accurate means of evaluating ventricular function (Fig. 13.1).
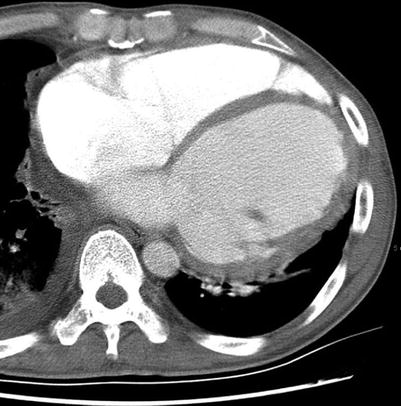
Fig. 13.1
CT of a patient with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. ECG-gated cardiac CT shows a dilated left ventricle (7 cm in the internal diameter)
13.2.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Detailed morphologic evaluation of ventricles.
In black blood images, enlarged cardiac chambers and thin myocardial walls are evident.
Mural thrombi can also be identified.
Functional evaluation of ventricles.
Cine images usually show ventricular hypokinesia and increased volumes. Using steady-state free precession (SSFP) images, the diagnosis of left ventricle (LV) dilation is simply made when short-axis internal LV chamber diameter is larger than 5.0 cm or when the LV end diastolic volume exceeds 235 mL or 112 mL/m2 in males and 174 or 99 mL/m2 in females.
The superior quality of images obtained by SSFP technique facilitates the detection of regional wall motion abnormalities allowing an easier differentiation between ischemic and non-ischemic LV impairment [7].
CMR is able to overcome many of the limitations of echocardiographic assessment of ventricular function and volumes. The significantly lower inter- and intraobserver variability in CMR measurements allows better monitoring of response to medical intervention or disease progression.
Characterization of myocardial tissue using late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) images.
To differentiate between DCM secondary to coronary artery disease and other causes of DCM. The differentiation between these subgroups may be fundamental in the therapeutic and prognostic approach to the patients [8].
In non-ischemic DCM, hyperenhancement was either absent (59–88 % of cases) or appeared as stripes of hyperenhancement in the mid-wall of the myocardium not related to specific coronary artery perfusion territories (9–35 % of the cases).
A subgroup of patients with DCM has fibrosis in a predominantly subendocardial distribution, characteristic of infarction (it has been suggested that these may represent coronary emboli-induced ischemic cardiomyopathy cases or ruptured coronary plaques that have subsequently recanalized).
Degree of fibrosis is an important prognostic predictor.
In a group of patients with DCM, 35 % of these patients had mid-wall myocardial fibrosis, which is a predictor of the combined end point of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular hospitalization and also of sudden cardiac death and ventricular tachycardia [9].< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


