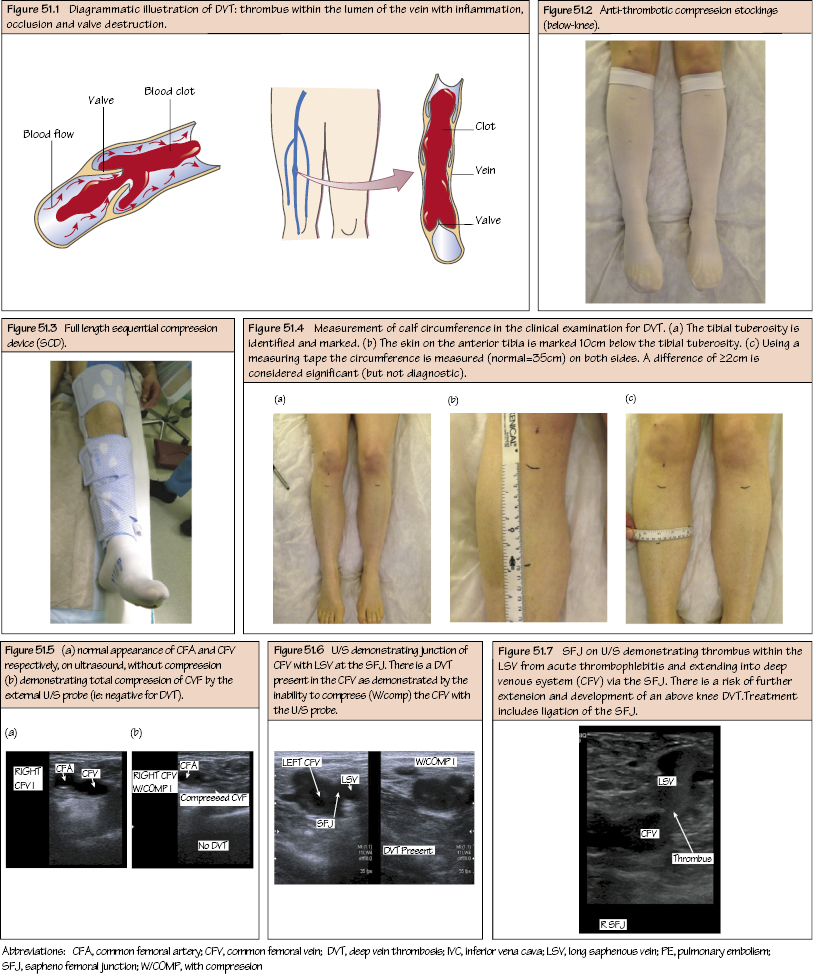
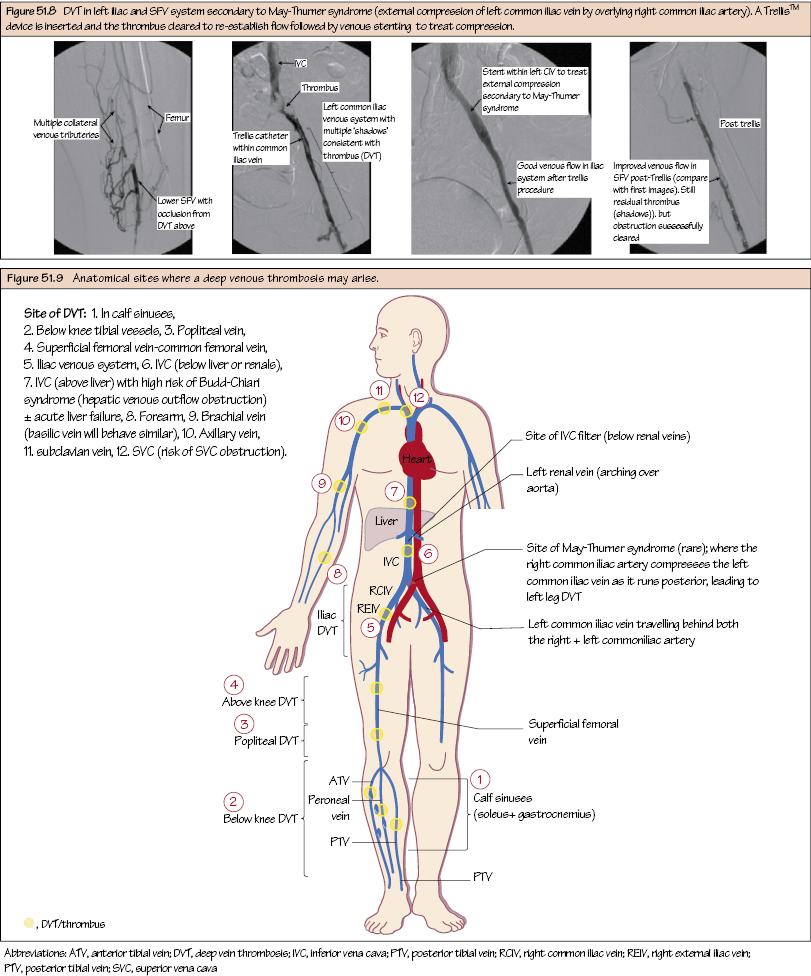
Deep Venous Thrombosis Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a thrombosis within the deep venous system. It most commonly affects the lower limb but may also include the iliac veins, IVC, SVC and upper limb veins. This is variable depending on the population but is estimated to occur in 10–30% of hospital patients and as high as 80% in critical illness and major trauma. They are more common in the left leg (longer pelvic course running behind both the right and left common iliac arteries). The majority develop in the BK segment including soleal sinuses, tibial veins and BK-popliteal vein. Fragmentation and embolisation is less common compared with an AK-DVT (AK-popliteal, SFV, CFV and iliac veins). An AK-DVT has a much higher incidence of PE and sudden death, but without treatment BK DVTs may propagate proximally.
Incidence
Risk Factors, Complications and Management of DVT
Risk Factors
Complications
Management
Prophylaxis
Treatment
Lower Limb DVT
Symptoms and Signs
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


