8 Complications Even minimally invasive interventional radiology involves certain risks (Table 8.1). One must be thoroughly familiar with them, weigh them against the expected benefit, and discuss them with the patient. The risks involve the access site, the site and type of treatment (percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, stent placement, etc.), and the entire body (systemic complications). When minor complications such as hematoma are included, then the overall rate is ~ 10%. The number and severity of all complications can be influenced by careful action (Cragen and Heuser 2008). The high number of local complications at the vascular access site can largely be attributed to errors in puncture, catheterization, and aftercare. A pseudoaneurysm usually occurs in the absence of a buttressing structure during compression. It is essentially caused by performing the puncture too far distal. Compression applied at the wrong place (to the superficial cannula track without compression of the wound in the vessel wall) is also conducive to pseudoaneurysm (see Chapter 3, Retrograde Catheterization of the Common Femoral Artery, p. 42 and Chapter 3, Treatment of the Access Site, p. 66). The risk also increases with the diameter of the sheath, the length of time the sheath remains in place, and impaired coagulation, and when the patient gets out of bed too soon. Table 8.1 Incidence of complications according to Pentecost et ala and Matsi and Manninenb
Complications at the Arterial Access Site
Pseudoaneurysm
| Complication rate (%) |
|
| Pentecost et al (1994) | Matsi and Manninen (1998) |
Complications at the arterial access site |
|
|
Bleeding or hematoma | 3.4 | 5.4 |
Pseudoaneurysm | 0.1 | 1.2 |
Arteriovenous fistula | 0.1 | 0.5 |
Retroperitoneal hematoma |
| 0.5 |
Local infection |
| 0.5 |
Complications at the percutaneous transluminal angiography or stent site | ||
Thrombosis | 3.2 | 1.4 |
Rupture or perforation | 0.3 |
|
Distal embolization | 2.3 | 2.2 |
Dissection | 0.4 |
|
Systemic complications |
|
|
Renal failure | 0.2 |
|
Myocardial infarction | 0.2 |
|
Cerebral insult | 0.55 |
|
Mortality | 0.2 |
|
aRetrospective study of 3,784 interventions.
bProspective study of 410 interventions.
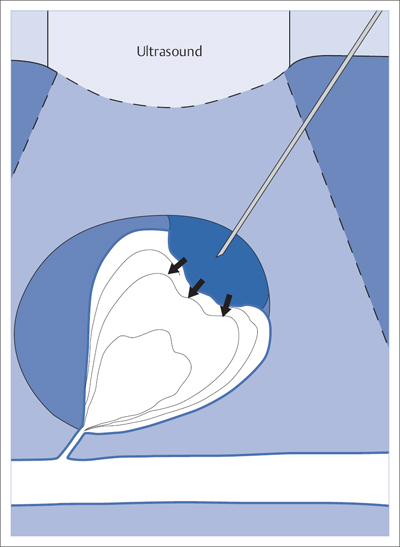
Fig. 8.1 Treatment of a pseudoaneurysm by injection of thrombin. During the slow injection, the color Doppler scan shows how the thrombus grows and fills the aneurysm within seconds. The flow signals disappear. Important: No thrombin must enter the artery!