63 Cardiac Tumors
Primary Benign Cardiac Tumors
The majority of benign cardiac tumors are myxomas; however, a wide variety of tumors arise within the heart (Table 63-1).
Table 63-1 Histologic Distribution of Primary Benign Cardiac Neoplasms
| Percentage of Tumors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Benign Tumor | Adults | Children |
| Myxoma | 45 | 15 |
| Lipoma | 21 | 0 |
| Papillary fibroelastoma | 16 | 0 |
| Rhabdomyoma | 2 | 45 |
| Fibroma | 3 | 15 |
| Hemangioma | 5 | 5 |
| Teratoma | 1 | 13 |
| Other | 6 | 6 |
With permission from Allard MF, Taylor GP, Wilson JE, et al. Primary cardiac tumors. In: Goldhaber S, Braunwald E, eds. Atlas of Heart Diseases. Philadelphia: Current Medicine; 1995:15.1–15.22.
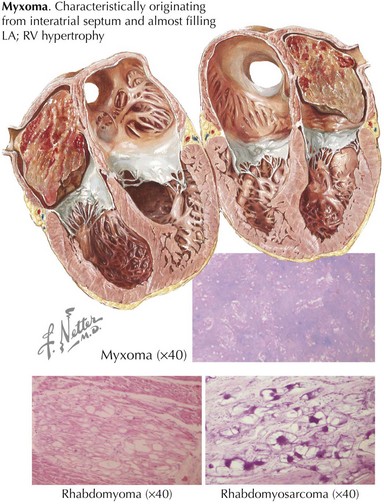
Myxoma
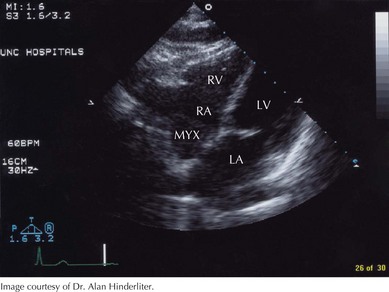
Myxomas are the most common primary cardiac neoplasm, accounting for 50% of all benign cardiac tumors (Fig. 63-1). There is a female predominance of 2 : 1 to 3 : 1, and the median age of presentation is 50 years, although myxomas can occur at any age. Myxomas arise in the left atrium 75% of the time, usually on the interatrial septum near the fossa ovalis. Right atrial myxomas account for 20% of tumors (Fig. 63-2). The balance of myxomas occur in either ventricle and, in rare cases, on the cardiac valves. The majority of myxomas (>90%) are solitary.