Chapter 48
Cardiac Tumors
1. Which are more common, primary cardiac tumors or metastatic tumors to the heart?
2. What are the most common tumors that metastasize to the heart?
3. What are the most common primary cardiac tumors?
Benign tumors are more common than malignant tumors, occurring approximately three times as often as malignant tumors. In children, 90% of primary cardiac tumors are benign. The most common benign cardiac tumors in adults are myxomas, accounting for approximately half of all primary cardiac neoplasms; other common benign cardiac tumors are lipomas and papillary fibroelastomas. Rhabdomyomas are the most common benign tumor occurring in infants and children. Interestingly, rhabdomyomas usually regress over time and do not require specific treatment in asymptomatic individuals. Primary and secondary (metastatic) tumors involving the heart are listed in Table 48-1.
TABLE 48-1
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY (METASTATIC) TUMORS INVOLVING THE HEART
Primary Tumors
Myxoma
Lipoma
Papillary fibroelastoma
Rhabdomyoma
Fibroma
Angiosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Lymphoma
Lipomatous hypertrophy
Secondary (Metastatic) Tumors
Lung (bronchogenic) cancer
Breast cancer
Esophageal cancer
Thyroid cancer
Melanoma
Lymphoma
Leukemia
Renal cell carcinoma
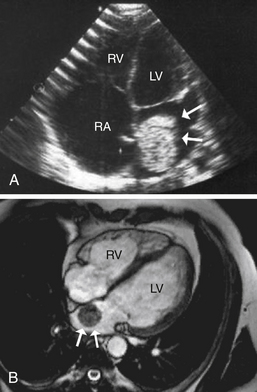
4. In what chamber do most myxomas occur?
Approximately 75% to 80% of myxomas occur in the left atrium (Fig. 48-1), with 15% to 20% occurring in the right atrium. Only 3% to 4% of myxomas arise in the left ventricle and 3% to 4% arise in the right ventricle. Myxomas are usually pedunculated and typically arise from the interatrial septum via a stalk. They are described on gross pathological examination as gelatinous in consistency. They most commonly occur between the third and sixth decades of life, and more frequently occur in women. They can cause effective obstruction of filling of the left or right ventricles, leading to left or right heart failure symptoms and findings, mimicking the symptoms and findings of mitral or tricuspid valve stenosis. Systemic embolism occurs in 30% to 40% of patients. Constitutional symptoms and findings (see Question 6) are also common. Most myxomas occur sporadically, but approximately 7% to 10% may be familial (see Question 10).