Fig. 30.1
(a) 2-D transesophageal echo: a large myxoma (Myxoma) is shown prolapsing along the anterior mitral valve leaflet (AL) and into the left ventricle during diastole. PL posterior mitral valve leaflet, LV Septum inter-ventricular septum, AoV aortic valve. (b) 3-D transesophageal echo: the same myxoma is shown en face along with the mitral valve. The myxoma obscures the right half of the anterior annulus as it is attached near the right fibrous trigone (RFT), LFT left fibrous trigone, P 1 , P 2 , P 3 posterior leaflet scallops
Papillary fibroelastomas comprise 10 % of all primary cardiac tumors. They are small frond-like, benign tumors that usually are attached to either the aortic or mitral valve leaflets. Their major risk is embolization, either to the coronary or cerebral circulation. In most circumstances they should be excised surgically, even in asymptomatic patients.
Robotic Excision of Cardiac Tumors
Left Atrial Myxomas
In the past most cardiac tumor extirpations have been done through a sternotomy incision. Some surgeons now prefer a right mini-thoracotomy with direct vision. Using robotic surgical technology, right and left atrial myxomas now can be removed by the least invasive methods. High-definition, magnified visualization and superior ergonomic robotic instrumentation provide surgeons excellent access with ease of extirpation.
Patients are intubated for single lung isolation and positioned as shown in Chaps. 3 and 23. Hemodynamic monitoring is also the same. Instrument port placement, the working incision, retraction, and perfusion techniques also are as in robotic mitral valve surgery. We use 8-mm robotic instruments to remove both right and left sided myxomas. Formerly, we excised both right and left atrial myxomas via the right atrium, crossing the inter-atrial septum. We approached the stalk from behind, gently delivering the tumor without fragmentation. Often a pericardial patch was required to repair the resulting defect. The dynamic robotic retractor now affords excellent access to the left atrial roof (inter-atrial septum) as well as the mitral valve and annulus. By manipulating retractor blades in multiple conformations, ideal access to the myxoma base or stalk can be attained through the left atriotomy. Moreover, residual septal defects can easily be closed from the left atrium, including patch closure. Septal excision usually introduces air into the right atrium causing venous drainage problems. Perfusionists can manage minor amounts of suctioned air very well if the superior vena cava is occluded with a temporary ligature and the lower venous cannula is withdrawn to below the liver.
In Fig. 30.2a (inset) a very large myxoma is shown to occupy the entire left atrium, obscuring the short pedunculated stalk. When the left atrium was opened, the myxoma obstructed views of most of the intra-atrial anatomy. The stalk was attached firmly to the mitral annulus, near the right fibrous trigone and not far from the major cardiac conduction system. The dynamic atrial retractor was positioned carefully to allow partial vision of the stalk (Fig. 30.2b).
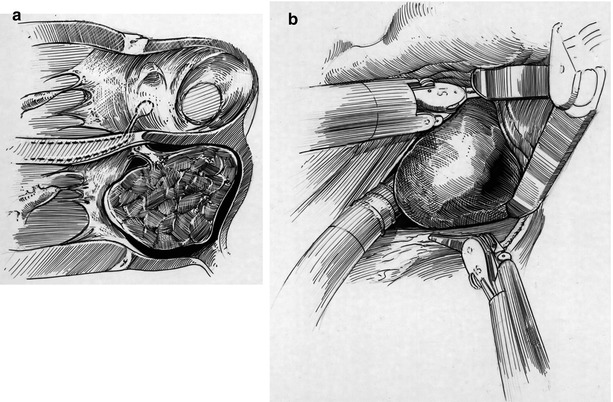

Fig. 30.2




(a) (Inset) Left atrial myxoma (Featured in Fig. 30.1) is shown attached to the anterior annulus, near the right fibrous trigone. The stalk extended deep into the central fibrous body and approached the conduction system as it passed into the ventricular septum. The atrio-ventricular node with the associated conduction system is shaded. (b) (Bottom) When the left atrium was opened and exposed using the dynamic robotic retractor, the myxoma occupied nearly the entire chamber obscuring the attached stalk. Robotic instruments gently displaced the tumor to the side, enabling access to the stalk. A suction drain is used to keep the operative field free of blood
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


