Chapter 11
Cardiac Positron Emission Tomography
1. What is positron emission tomography (PET)?
2. Which are the two most common PET radiopharmaceuticals used for myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI)?
Rubidium-82 (Rb-82) and nitrogen-13 (N-13) ammonia.
3. What are the characteristics of Rb-82?
Rb-82 is a monovalent cation analog of potassium. It is commercially available as a strontium-82 generator. Its physical half-life is 75 seconds. It is extracted with high efficiency by myocardial cells through the Na+,K+-ATPase pump. The adult radiation dose from a Rb-82 MPI varies from 1.75 to 7.5 mSv (Fig. 11-1).
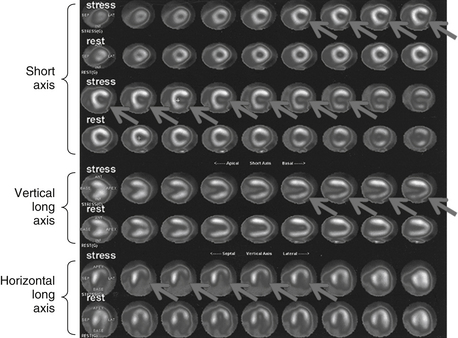
Figure 11-1 Abnormal Rb-82 myocardial perfusion imaging demonstrating inducible ischemia of left circumflex vascular territory. The figure shows stress and rest images displayed in three planes: short axis (apex to base), vertical long axis (septum to lateral wall), and horizontal long axis (from inferior to anterior). The rest images demonstrate good perfusion throughout the left ventricle. The stress images demonstrate decreased tracer in the lateral wall (arrows). (Modified with permission from Branch KR, Caldwell JH, Soine LS, et al: Vascular [humoral] cardiac allograft rejection manifesting as inducible myocardial ischemia on nuclear perfusion imaging, J Nucl Cardiol. 12(1):123-124, 2005.)
4. What are the characteristics of N-13 ammonia?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


