A Left vertebral artery arises from the aortic arch
B. Left common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic artery
C. Left subclavian artery arises from the brachiocephic artery
D. Right common carotid arises from the aortic arch
E. Right subclavian artery arises from the descending aorta
24. What is the sinus that lies anterior to the superior vena cava and posterior to the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk called?
A. Transverse sinus
B. Oblique sinus
C. Coronal sinus
D. Pericardial recess
E. Longitudinal sinus
25. A 2-year-old female with a history of a ventricular septal defect presents to your office for follow-up. On examination, you hear a diastolic murmur at the apex. Echocardiography confirms that she has an infundibular or subarterial type of VSD, with aortic regurgitation. Prolapse of which aortic cusp is most likely causing the regurgitation?
A. Left
B. Right
C. Anterior
D. Septal
E. Noncoronary
26. An overriding AV valve:
A. Has chordal attachments into both ventricles
B. Must have chordal attachments to the ventricular septal crest
C. Empties into two ventricles
D. Cannot coexist with straddling
E. Is never associated with malalignment type of VSD
27. Which of the following is true about a straddling cardiac valve?
A. Cannot coexist with overriding
B. Is not associated with malalignment type of VSD
C. Is most commonly involving the pulmonary valve
D. Is a common component of TOF
E. Involves anomalous insertion of chordae tendineae
28. You diagnose a neonate with asplenia syndrome. Which of the following is most likely to be present in this patient?
A. The liver is midline with two mirror-image left lobes
B. The biliary tree is patent with associated multiple gall bladders
C. Stomach position is fixed to the right side
D. Normal rotation of the bowels
E. Descending aorta and IVC are on the same side of vertebral column
29. You diagnose a neonate with polysplenia. Which of the following is true regarding this patient?
A. The situs of abdominal viscera is almost always ambiguous
B. There are multiple spleens on both the left and right sides
C. The IVC is typically interrupted, with azygous continuation to SVC
D. Multiple gallbladders are common
E. The SVC is typically interrupted
30. Which is the most reliable feature of the normal AV valve that distinguishes the mitral valve from the tricuspid valve?
A. Shape of the orifice
B. AV valve—semilunar valve continuity
C. Presence of septal chordal attachments
D. Level of attachment of AV valve at cardiac crux
E. Number of leaflets
31. A neonate is diagnosed with double-outlet right ventricle (DORV). Which of the following positions of the aorta are you most likely to find (relative to the pulmonary artery)?
A. Side by side
B. Right anterior
C. Left anterior
D. Left posterior
E. Right posterior
32. A neonate is diagnosed with pulmonary atresia/VSD. The patient undergoes a cardiac catheterization. What do you tell the interventionalist is the most common origin for systemic-to-pulmonary collaterals in this diagnosis?
A. Ascending thoracic aorta
B. Descending thoracic aorta
C. Abdominal aorta
D. Left subclavian artery
E. Coronary artery
33. A single SA node in a normal position is typically found in which of the following?
A. Left juxtaposition of the atrial appendages
B. Right juxtaposition of the atrial appendages
C. Right atrial isomerism
D. Left atrial isomerism
E. Situs inversus of the atria
34. What is the crescent-shaped valvular remnant at the coronary sinus ostium called?
A. Thebesian valve
B. Eustachian valve
C. Valve of the fossa ovalis
D. Chiari network
E. Valve of the SVC
35. Mutations in which protein may cause disassociation of the intracellular cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix in cardiac myocytes, in addition to causing muscular dystrophy?
A.α-Dystroglycan
B. Syntrophin
C. Cytoplasmic actin
D. Dystrophin
E. Caveolin
36. From what does closure of the foramen ovale shortly after birth result directly or indirectly?
A. Endothelial release of prostaglandin
B. Endothelial release of prostacyclin
C. Smooth muscle contraction within the septum secundum
D. Postnatal decline of pulmonary vascular resistance
E. Decreased right ventricular compliance
37. Among the following fetal venous structures, which has the lowest oxygen saturation?
A. Ductus venosus
B. Inferior vena cava
C. Left hepatic vein
D. Coronary sinus
E. Right pulmonary vein
38. A 6-month-old infant status post repair of a complete AV canal has the following results of a blood gas:
pCO2: 36 mm Hg
HCO3: 14 mm/L
pH: 7.21
Which of the following is the acid–base abnormality present in this patient?
A. Acute respiratory alkalosis
B. Acute respiratory acidosis
C. Acute metabolic acidosis
D. Acute metabolic alkalosis
E. Chronic respiratory acidosis
39. The direction in which blood flows through an ASD primarily is related to what?
A. Relative compliances of the LV and RV
B. Pulmonary vascular resistance
C. Systemic vascular resistance
D. Morphology of Eustachian valve
E. Redundancy of atrial septum
40. Which of the following events is responsible for early, functional closure of the patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
A. Hemorrhage and necrosis in the subintimal region
B. Medial smooth muscle cell migration into the wall of the ductus
C. Equalization of pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance
D. Infolding of the endothelium
E. Thinning of the intimal layer
41. A 12-year-old male is referred to you for a murmur. On taking the history, you find out that he is a recent immigrant from Nepal, just arriving yesterday. Which of the following are you most likely to find on a hemodynamic evaluation of this patient, compared to a patient living at sea level?
A. Elevated pulmonary artery pressure
B. Left atrial enlargement
C. Decreased LV systolic function (EF ~40%)
D. Decreased tricuspid regurgitant velocity
E. Elevated systemic blood pressure
42. What does the formation of an ostium primum ASD result from?
A. Abnormal endocardial cushion development
B. Excessive resorption of the septum primum
C. Insufficient growth of the septum secundum
D. Abnormal resorption of the pulmonary vein
E. Abnormal rotation of the dextrodorsal conal swelling
43. The normal left aortic arch is primarily derived from which embryologic aortic arch?
A. First (I) arch
B. Second (II) arch
C. Third (III) arch
D. Fourth (IV) arch
E. Sixth (VI) arch
44. In the cardiac sarcomere, which of the following named feature includes the entirety of the myosin contractile elements?
A. E-line
B. I-band
C. H-zone
D. Z-disk
E. A-band
45. The resting potential of which ion is primarily responsible for the baseline (phase 4) resting conductance of cardiac myocytes?
A. Calcium
B. Sodium
C. Potassium
D. Chloride
E. Magnesium
46. The rapid depolarization of cardiac myocytes (phase 0) is driven by the rapid influx of which ion into the myocytes?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Chloride
D. Magnesium
E. Calcium
47. An 8-year-old male is diagnosed with a sinus venosus ASD on echocardiography. Relative to the fossa ovalis, where would you expect to find a sinus venosus ASD?
A. Anterior and superior
B. Anterior and inferior
C. Posterior and superior
D. Posterior and inferior
E. Anterior and apical
48. Atrial systole accounts for what percentage of ventricular filling in the normal patient?
A. <1%
B. 5%
C. 15%
D. 75%
E. 90%
49. A 3-year-old female is diagnosed with Ebstein’s anomaly. Of the following, which additional diagnosis is most likely to be found in this patient?
A. Ventricular septal defect
B. Coarctation of the aorta
C. PDA
D. Mitral valve prolapse
E. Pulmonary stenosis
50. Which of the following structures are specialized cell junctions between adjacent myocytes and include fascia adherens, desmosomes, and gap junctions?
A. Z-disks
B. Intercalated disks
C. Costameres
D. T-tubules
E. Sarcolemma
51. Which of the following structures typically pass under the transverse aortic arch in the normal heart?
A. Right pulmonary artery and right bronchus
B. Left pulmonary artery and left bronchus
C. Left pulmonary artery and right bronchus
D. Right pulmonary artery and left bronchus
E. Left pulmonary artery and thoracic duct
52. A 3-year-old girl undergoes repair of coarctation of the aorta. Post-operatively, she is able to be extubated, but develops intermittent stridor. Chest radiography is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely structure that was injured during the operation?
A. Left vagus nerve
B. Right recurrent laryngeal nerve
C. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
D. Thoracic duct
E. Right vagus nerve
53. The normal right superior vena cava is derived from which of the following embryologic structures?
A. Right anterior cardinal vein
B. Left anterior cardinal vein
C. Right vitelline vein
D. Ductus venosus
E. Left umbilical vein
54. Which of the following embryologic aortic arches regresses and typically does not contribute to any structure in the normal neonate?
A. Left fourth arch
B. Right fourth arch
C. Left third arch
D. Left sixth arch
E. Left fifth arch
55. Systemic arteriolar vasodilation occurs in response to:
A.Decreased pO2
B.Decreased pCO2
C.Decreased H+
D.Decreased K+
E.Decreased Mg++
56. A term neonate presents with tachycardia, poor perfusion, and respiratory failure. The liver is enlarged on examination. Echocardiography reveals dilation of all four heart chambers. You note that the echo-calculated cardiac output is markedly elevated. Which of the following is the most likely source of the high-output cardiac failure?
A. Lower extremity arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
B. Vein of Galen malformation
C. Upper extremity AVM
D. Hepatic AVM
E. Pulmonary AVM
57. A 14-year-old male presents with shortness of breath and progressive fatigue over the previous 2 to 3 years. He denies any chest pain, syncope, wheezing, or chronic cough. His past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. While performing an echocardiogram, you note the Doppler flow pattern in the descending aorta seen in Figure 1.2.
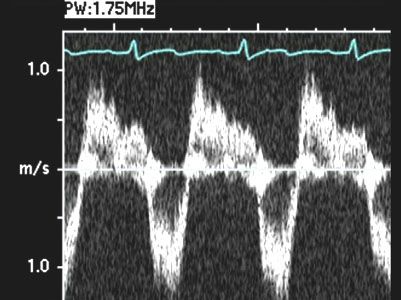
You note that there is no evidence of a ductus arteriosus or aortic insufficiency, and flow to the cranial vessels is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ascending aorta dilation
B. Mitral regurgitation
C. Aberrant right subclavian artery from the descending aorta
D. LV-aorta tunnel
E. Anomalous RCA from the left sinus
58. A newborn infant presents with TOF. Of the following abnormal coronary patterns, which are you most likely to find on echocardiography?
A. Intramural left coronary artery
B. Left anterior descending from the RCA
C. Left circumflex artery from the RCA
D. Single left coronary artery
E. Single RCA
59. A 3-day-old female is diagnosed with tricuspid atresia. Which of the following great artery relationships are you most likely to find on echocardiography?
A. D-TGA
B. L-TGA
C. Normally related great arteries
D. Left anterior aorta
E. Right anterior aorta
60. Which of the following is true regarding the morphologic left atrium in the normal heart?
A. It contains the limbus of the fossa ovalis
B. There is a large, pyramidal appendage
C. There are pectinate muscles
D. There is a prominent crista terminalis
E. There is a small, fingerlike appendage
61. You are seeing a 4-month-old female with tricuspid atresia, d-TGA, moderate pulmonary stenosis, and a mildly restrictive ventricular septal defect. In this patient, where is the AV node most likely to be positioned?
A. Floor of the blind right atrium
B. Posteriorly behind the ostium of the coronary sinus
C. Anteriorly along the atrial septum in the right atrium
D. In the left atrium just medial to the left AV valve annulus
E. Lateral to the ostium of the IVC in the right atrium
62. Which of the following is true regarding the right ventricle in the normal heart?
A. Has small apical trabeculations
B. Has a prominent crista terminalis
C. Has a smooth upper septal surface
D. Is a tripartite chamber
E. There is tricuspid-pulmonary continuity
63. At 1 month of gestation in the human embryo, the pulmonary venous plexus establishes a single connection to the sinoatrial portion of the developing heart, called the common pulmonary vein. What is the fate of this structure in the normal heart?
A. Disappears, with eventual independent appearance of the four pulmonary veins
B. Is incorporated into the back wall of the left atrium
C. Is incorporated into the coronary sinus
D. Is incorporated into the wall of the right atrium
E. Becomes the supero-posterior portion of the atrial septum
64. Migration of cardiac neural crest cells into the developing heart induces which embryologic process?
A. Rightward looping of the primitive heart tube
B. Endocardial cushion development
C. Septation of the conotruncal outflow tract
D. Septation of the atria
E. Differentiation between atria and ventricles
65. A 14-year-old male presents with cyanosis. An echocardiogram reveals severe Ebstein’s anomaly with severe tricuspid valve regurgitation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his cyanosis?
A. Left to right shunt at atrial level
B. Right to left shunt at ventricular level
C. Coronary fistula
D. Stenotic outflow to pulmonary arteries
E. Right to left shunt at atrial level
66. You are called to see a cyanotic neonate in the neonatal intensive care unit. You note that the patient has an oxygen saturation of 69%. His chest x-ray shows decreased vascular markings in the lung fields. Which of the following is the most likely anatomy you will find on examination and echocardiogram?
A. Critical pulmonary stenosis
B. Truncus arteriosus
C. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
D. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
E. Tricuspid atresia with transposed great arteries
67. Which of the following is true regarding fetal hemoglobin?
A.Is composed of α– and β-subunits
B. Is present in normal children until the age of 6 years
C. Is replaced by adult hemoglobin by the 38th week of gestation
D. Has a higher affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin
E. Has a lower affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin
68. A 4-month-old infant status post repair of a ventricular septal defect has the following results of a blood gas:
pCO2: 73 mm Hg
HCO3: 25 mm/L
pH: 7.15
Which of the following is the acid–base abnormality present in this patient?
A. Acute respiratory alkalosis
B. Acute respiratory acidosis
C. Acute metabolic acidosis
D. Acute metabolic alkalosis
E. Chronic respiratory acidosis
69. Relative to the fossa ovalis, where would you expect to find a coronary sinus ASD?
A. Anterior and superior
B. Anterior and inferior
C. Posterior and superior
D. Posterior and inferior
E. Posterior and medial
70. Which of the following changes occurs with inspiration in the normal heart and lungs?
A.Increase in pleural pressure by 3 to 5 cm-H2O
B. Decrease in intra-abdominal pressure
C. Decreased Doppler E velocity of the tricuspid valve
D. Increased Doppler E velocity of the mitral valve
E. Increased in right ventricular stroke volume
71. A 3-year-old female is in the ICU status post modified Fontan operation and has poor-perfusion and desaturations. When negative-pressure ventilation is instituted, her saturations improve markedly. Which of the following is the most accurate explanation for this improvement?
A. The Fontan circulation is more dependent on inspiratory increases in cardiac output compared to a normal circulation
B. Improvement in atelectasis
C. Improved flow through the Fontan fenestration
D. Associated left (systemic) ventricular dysfunction
E. The Fontan circulation is more dependent on expiratory increases in cardiac output as compared to a normal circulation
72. A circular structure is seen on a transesophageal echocardiogram running between the left pulmonary veins and the left atrial appendage, just posterior and superior to the mitral valve. What does this structure most likely represent?
A. Membrane of cor triatriatum
B. Persistent levo-atrial cardinal vein
C. Persistence of the left horn of the sinus venosus
D. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
E. Descending aorta
73. Which fetal remnant delivers blood from the right and left hepatic veins to the right atrium?
A. Ductus arteriosus
B. Foramen ovale
C. Ductus venosus
D. Aortic isthmus
E. Umbilical arteries
74. Of the following, which structure in the fetus has the least saturated blood?
A. Superior vena cava
B. Inferior vena cava
C. Patent ductus arteriosus
D. Ductus venous
E. Ascending aorta
75. The leftward and superior position of the Eustachian valve benefits fetal life by which of the following?
A. Directing oxygen-poor blood to the tricuspid valve
B. Directing oxygen-rich blood through the foramen ovale
C. Directing oxygen-rich blood from the superior vena cava
D. Directing oxygen-rich blood from the coronary sinus
E. Directing oxygen-poor blood from the inferior vena cave
76. In fetal life, what percent of the total cardiac output is derived from the right ventricle?
A. 10%
B. 25%
C. 40%
D. 60%
E. 90%
77. What fetal remnant diverts right ventricle blood from the lungs to the descending aorta?
A. Ductus arteriosus
B. Foramen ovale
C. Ductus venous
D. Aortic isthmus
E. Vitelline veins
78. On average, at what age will the normal infant’s mean pulmonary arterial pressure decrease to half of their systemic arterial pressure?
A. 2 hours of life
B. 12 hours of life
C. 1 day of life
D. 2 weeks of life
E. 2 months of life
79. On fetal echocardiogram, you diagnosed a fetus with pulmonary atresia. All blood in their right ventricle is directed through the foramen ovale to the left atrium. What is the most likely consequence of the total cardiovascular output going through the left ventricle in this patient?
A. Aortic diameter greater than normal
B.In utero left ventricular failure
C. Under-development of the right ventricle
D. Large patent ductus arteriosus
E. Increased oxygen delivery to the brain
80. The sarcomere is the fundamental contractile unit of striated muscle. Which contractile protein binds to calcium, allowing cross bridges to form and permitting contraction?
A. Actin
B. Myosin
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


