The bundle of His divides into left and right bundle branches. These facilitate very rapid activation of the left and right ventricles. Block in conduction through one or other bundle branch results in delayed and disordered activation of ventricular myocardium, as evidenced on the ECG by a ventricular complex which is prolonged in duration and has an abnormal configuration.
Right bundle branch block
ECG appearance
In right bundle branch block there is delay in activation of the right ventricle, while activation of the interventricular septum and free wall of the left ventricle and hence the initial part of the QRS complex is normal (Figure 4.1). Delayed right ventricular activation results in:
Figure 4.1 Right bundle branch block. There is an M-shaped complex in V1 and a deep slurred S wave in lead V6.
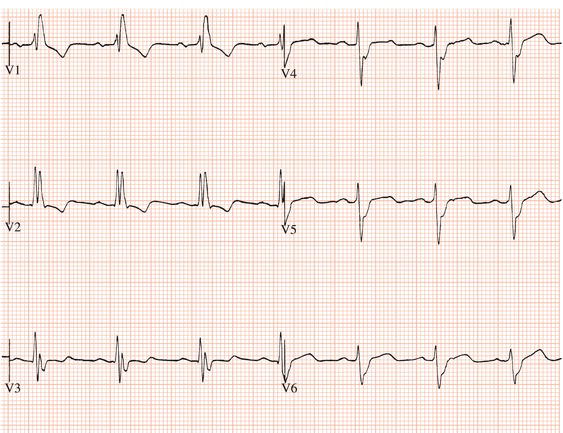
Partial right bundle branch block results in a similar ECG appearance but the QRS duration is 0.10 or 0.11 s.
Causes and significance
Right bundle branch block may be an isolated congenital lesion. It often occurs in congenital heart disease, in other causes of right ventricular hypertrophy or strain such as obstructive airways disease, and where there is myocardial damage. Right bundle branch block is common when there is disease of the specialised conducting tissues.
Based on limited data, neither pre-existing nor acquired right bundle branch block are of prognostic significance. However, a recent long-term survey has demonstrated a four-fold increased risk of developing AV block.
Extrasystoles and tachycardias of supraventricular origin may encounter a right bundle branch that is refractory to excitation and be conducted to the ventricles with a right bundle branch block pattern.
Left bundle branch block
ECG appearance
In left bundle branch block, activation of the interventricular septum is in the opposite direction to normal (i.e. from right to left), being initiated by an impulse arising from the right bundle branch. Thus:
Figure 4.2 Left bundle branch block. There is a broad positive complex in V6. There is no M-shaped complex in lead V1. The QS complex in V1 is also characteristic of left bundle branch block.
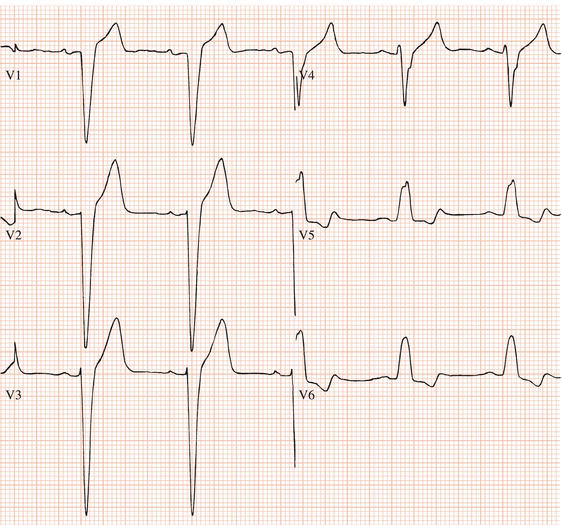
Partial left bundle branch block has a similar ECG appearance to complete left bundle branch block, but the QRS duration is 0.10 or 0.11 s.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


