FiO2 by 0.05-.10 increments
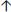 PEEP by 2–3 cm H2O
PEEP by 2–3 cm H2O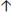 I:E ratio by changing the inspiratory time (Ti)
I:E ratio by changing the inspiratory time (Ti)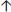 Suctioning of secretions
Suctioning of secretionsHigh PaO2 (O2 saturation)
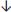 FiO2 in 0.05-.10 decrements
FiO2 in 0.05-.10 decrements
Acidosis/PACO2 increased
Secondary to 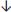
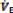 (
(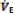 =VT x RR. Normal range is 5–8L/min)
=VT x RR. Normal range is 5–8L/min)
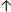 VT by 1–2ml/kg IBW per hour (not higher than 10 ml/kg IBW)
VT by 1–2ml/kg IBW per hour (not higher than 10 ml/kg IBW)
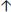 RR by 2–3 but do not exceed 35 breaths/min
RR by 2–3 but do not exceed 35 breaths/min
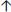 Peak pressure (on pressure support) to increase VT by 1–2 ml/kg IBW
Peak pressure (on pressure support) to increase VT by 1–2 ml/kg IBW
Secondary to trauma, sepsis, burns, or high carbohydrates
- Correct underlying etiology
- Change diet to low carbohydrate, high fat
Alkalosis/PACO2 decreased
Secondary to 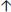
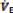
 RR by 2–3 breaths per minute
RR by 2–3 breaths per minute
 VT by 1–2ml/kg IBW
VT by 1–2ml/kg IBW
 Peak pressure (on pressure support) by 5 cmH2O
Peak pressure (on pressure support) by 5 cmH2O
Secondary to  RR from anxiety, pain, CNS disorders
RR from anxiety, pain, CNS disorders
 sedation
sedation
 pain medication
pain medication
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


