3.2 AV Conduction Disorders
1st Degree AV Block
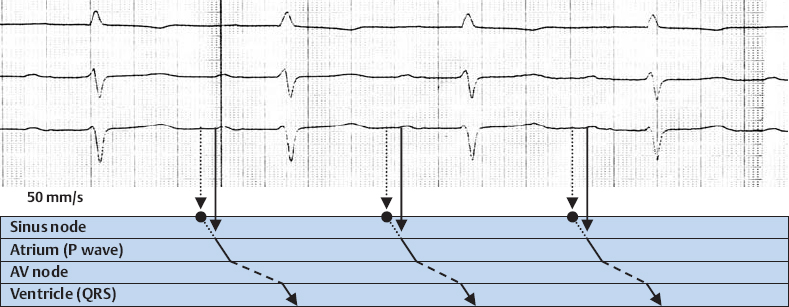
1st Degree AV Block
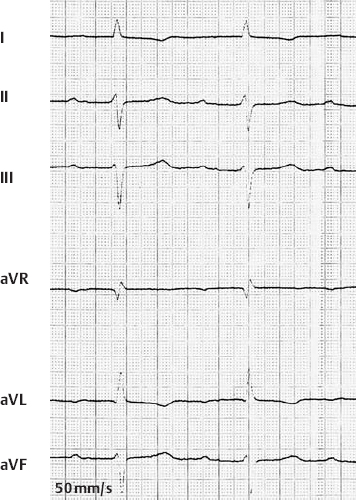
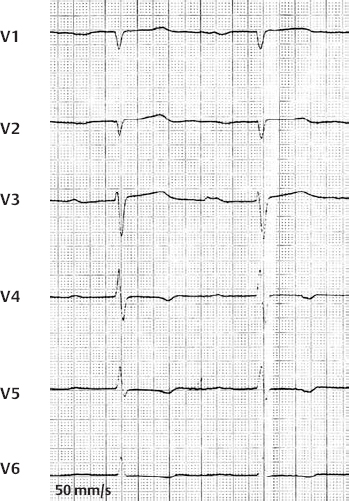
1st Degree AV Block
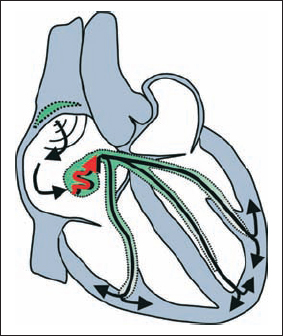
1st Degree AV Block with Complete Left Bundle Branch Block
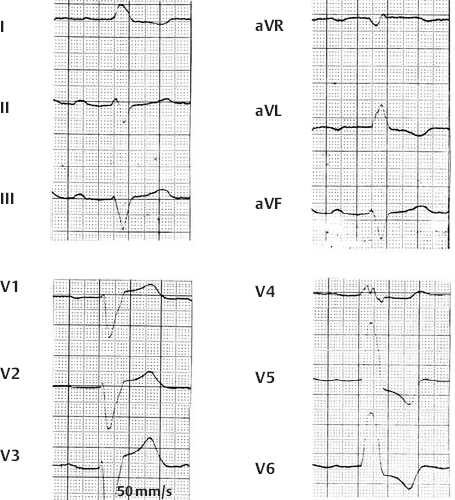
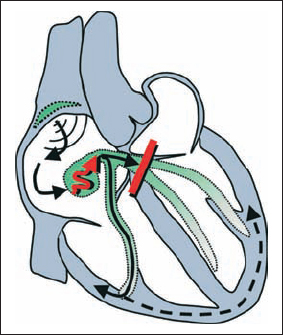
1st Degree AV Block with Complete Left Bundle Branch Block
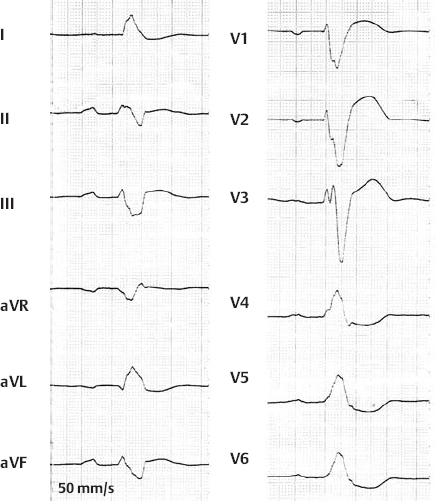
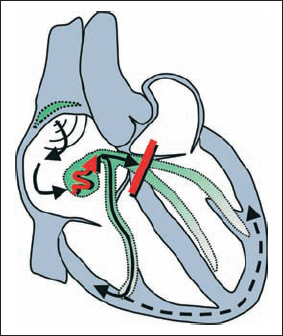
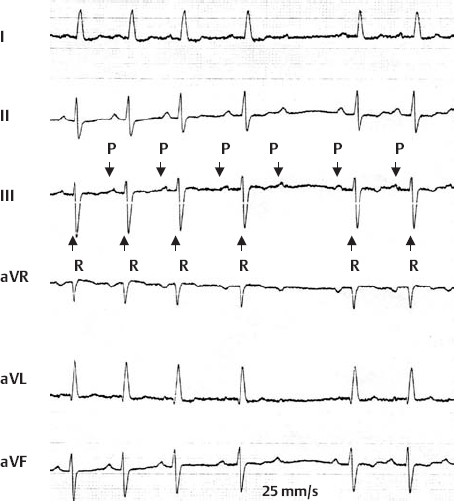
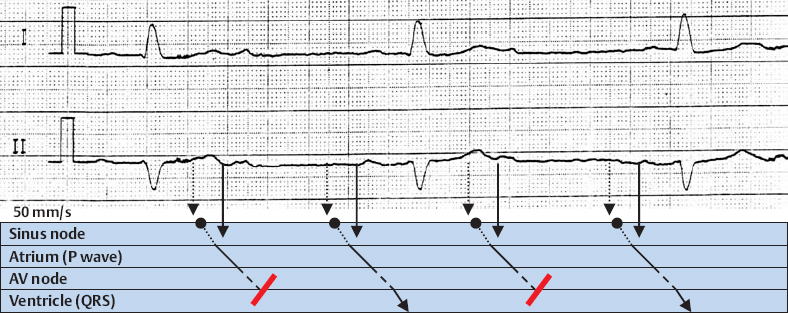
2nd Degree AV Block, Wenckebach Type
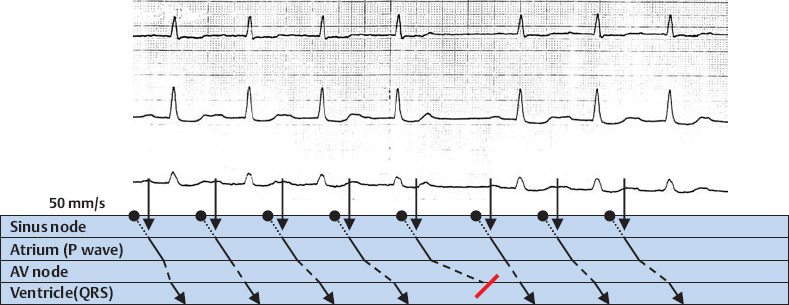
2nd Degree AV Block, Wenckebach Type
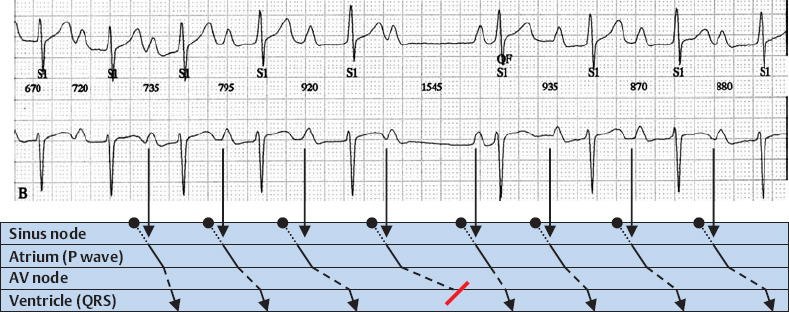
2nd Degree AV Block, Wenckebach Type
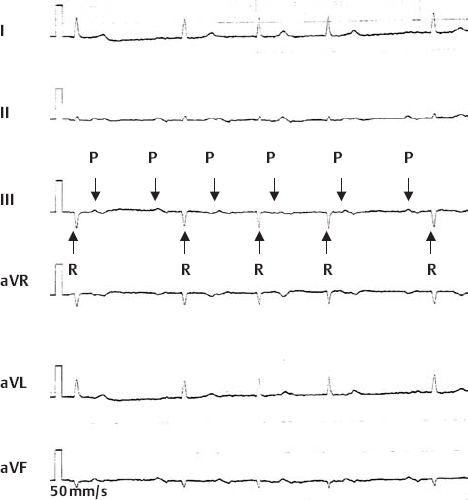
2nd Degree AV Block, Wenckebach Type
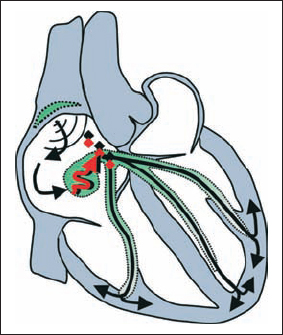
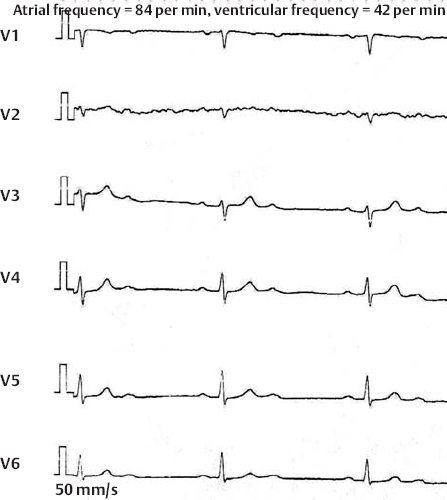
2nd Degree AV Block, 2:1 Block
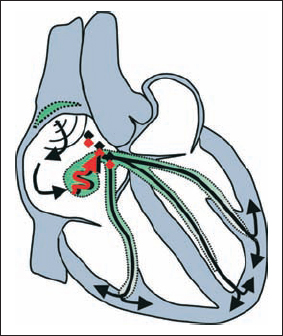
2nd Degree AV Block, Mobitz Type
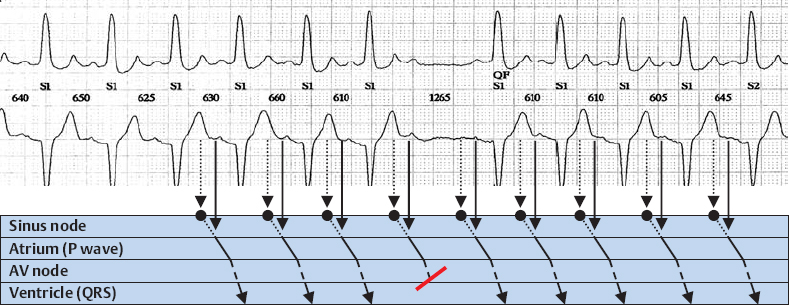
2nd Degree AV Block, 2:1 Block
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


