Intermittent PVCs (with low stroke volume and hence low pulse wave) followed by compensatory pause can cause ascertainment of HR by palpation of radial pulse to be artifactually low
| ||||||||||||||
3° AV block: atrial pacemaker unable to capture ventricles, subsidiary pacemaker emerges; distinguish from isorhythmic dissociation (A ≈V rate, some P waves nonconducting)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
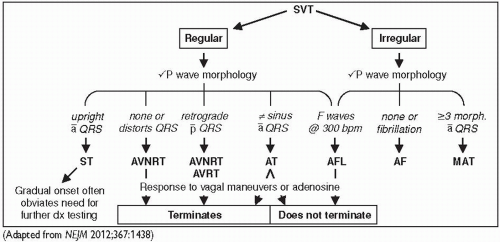 Figure 1-8 Approach to SVT |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accessory pathway (bypass tract) of conducting myocardium connecting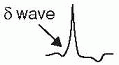 atria & ventricles, allowing impulses to bypass normal AVN delay
atria & ventricles, allowing impulses to bypass normal AVN delay
Preexcitation (WPW) pattern: ↓ PR interval, ↑ QRS width w/ δ wave (slurred onset, can be subtle), ST & Tw abnl (can mimic old IMI);
only seen w/ pathways that conduct antegrade (if pathway only conducts retrograde then ECG will be normal during SR; “concealed” bypass tract)
WPW syndrome: accessory pathway + paroxysmal tachycardia
Orthodromic AVRT: narrow-complex SVT (typically), conducting ↑ AVN & ↑ accessory pathway; requires retrograde conduction and can occur w/ concealed bypass tracts
can occur w/ concealed bypass tracts
Antidromic AVRT (less common): wide-complex regular tachycardia, conducting ↓ accessory pathway & ↑ AVN. Can meet many ECG morphology criteria for VT. Requires antegrade conduction and should see WPW pattern during SR.
should see WPW pattern during SR.
AF/AFL w/ conduction down accessory pathway: need to Rx arrhythmia and ↑ pathway refractoriness; use procainamide, ibutilide, or DCCV; avoid CCB & βB, dig/adenosine (can ↓ refractoriness of pathway → ↑ vent. rate ↑ VF)
Consider RFA if asx but AVRT or AF inducible on EPS (NEJM 2003;349:1803) or if rapid conduction possible ([check mark] w/ EPS if preexcitation persists despite exercise testing).
Disorganized atrial electrical activity → ineffective atrial mechanical contraction
For paroxysmal AF, >90% triggered by rapid firing in pulmonary veins (NEJM 1998;339:659)
Acute (up to 50% w/o identifiable cause)
Metabolic: high catecholamine states (stress, infection, postop, pheo), thyrotoxicosis
Drugs: alcohol (“holiday heart”), cocaine, amphetamines, theophylline, caffeine
Neurogenic: subarachnoid hemorrhage, ischemic stroke
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consider pharm or electrical cardioversion w/ 1st AF episode or if sx; if AF >48 h, 2-5% risk stroke w/ cardioversion (pharmacologic or electric) either TEE to r/o thrombus or ensure therapeutic anticoagulation for ≥3 wk prior if need to cardiovert urgently, anticoagulate acutely (eg, IV UFH)
either TEE to r/o thrombus or ensure therapeutic anticoagulation for ≥3 wk prior if need to cardiovert urgently, anticoagulate acutely (eg, IV UFH)
Likelihood of success ∝ AF duration & atrial size; control precip. (eg, vol status, thyroid)
Consider pre-Rx w/ antiarrhythmic drugs (eg, ibutilide), espec if 1st cardioversion fails
For pharmacologic cardioversion, class III and IC drugs have best proven efficacy
No clear survival benefit or ↓ stroke risk vs rate control (NEJM 2002;347:1825 & 2008;358:2667)
Consider if symptomatic w/ rate control (eg, heart failure), difficult to control rate, or tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


 use procainamide, ibutilide or amiodarone
use procainamide, ibutilide or amiodarone
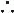 attention to anticoag Pulm, liver, thyroid toxicity [check mark] PFTs,
attention to anticoag Pulm, liver, thyroid toxicity [check mark] PFTs,  → warfarin by ˜50%
→ warfarin by ˜50%