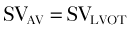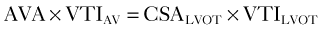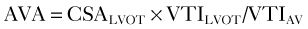3 Aortic Valve and Aortic Root
Anatomy and Function
Key Points
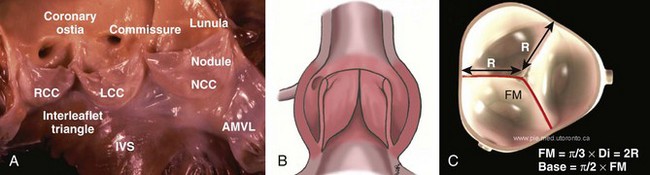
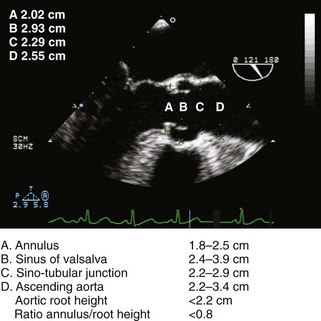
Normal Aortic Valve and Root Anatomy and Function
Congenital Anomalies of Cusp Number
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
Unicuspid and Quadracuspid Aortic Valve
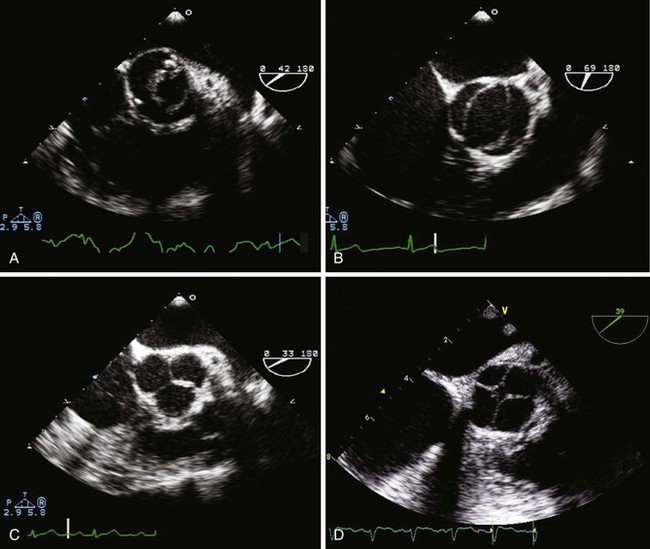
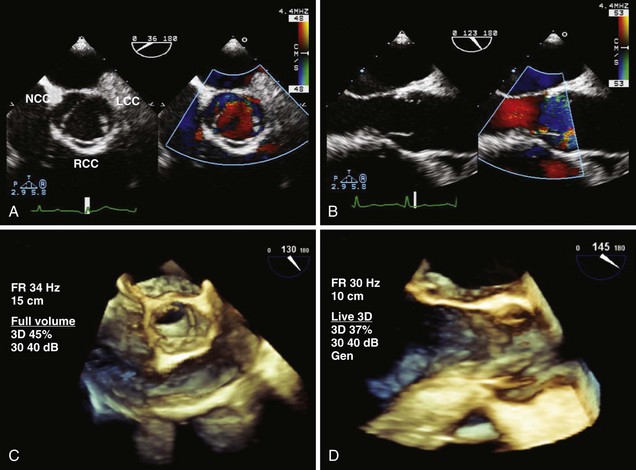
Echocardiographic Imaging of the Aortic Valve and Root
TABLE 3-1 BEST VIEWS FOR ASSESSING THE AORTIC VALVE
AR, aortic regurgitation; AV, aortic valve; AVA, aortic valve area; LAX, long axis; LCC, left coronary cusp; LVOT, left ventricular outflow tract; ME, midesophageal; NCC, noncoronary cusp; RCC, right coronary cusp; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract; SAX, short axis; 3D, three-dimensional; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; TG, transgastric; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography; 2D, two-dimensional.
Aortic Stenosis
Key Points
Etiology of Aortic Stenosis
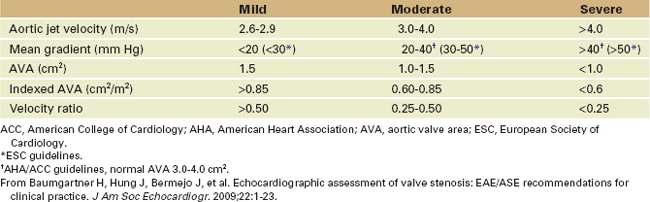
Step 1: Determine the Etiology
Features of Valvular AS
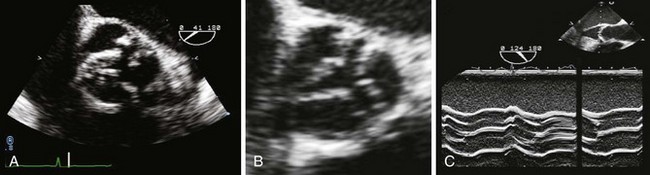
Calcific AS is typified by calcification within the central part of each cusp without commissural fusion, resulting in a stellate-shaped systolic orifice (Figure 3-6).
Rheumatic AS is characterized by commissural fusion with thickening and calcification along the cusp edges resulting in a triangular systolic orifice, almost always accompanied by rheumatic mitral valve (MV) changes (see Figure 3-6).
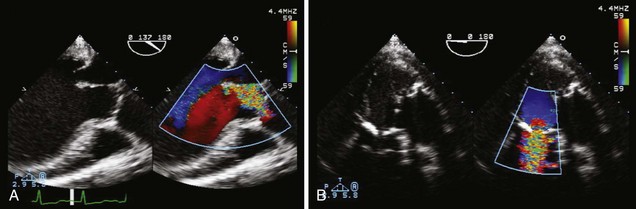
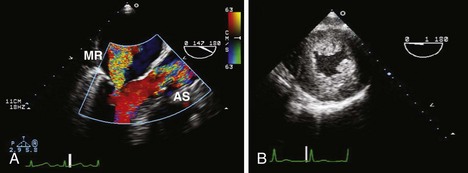
Associated findings with AS (Figure 3-7) are important to identify including MR, LVH with variable ventricular function, and aortic root dilatation. Their presence may affect the type and timing of intervention.
Quantitative Assessment of Aortic Stenosis
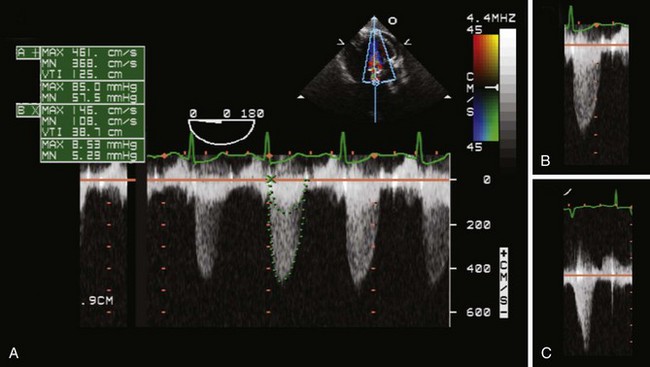
Step 2: Assess AS Jet Velocity
Step 3: Assess Transaortic Pressure Gradient
Pitfalls: Factors Affecting the Pressure Gradient
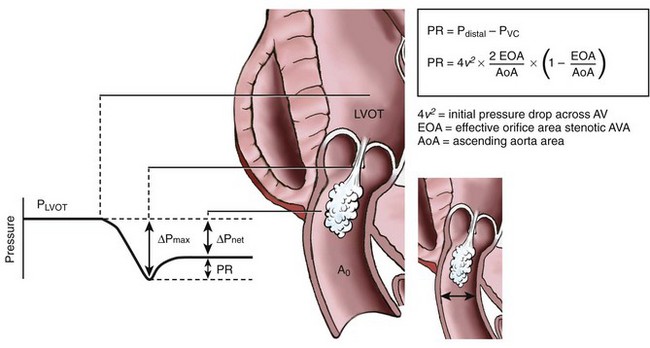
Pressure Recovery
Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction
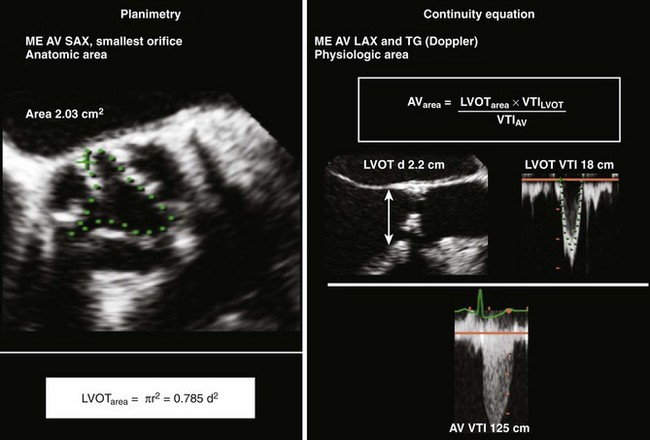
Step 4: Calculate Valve Area
Grading Aortic Stenosis
Step 5: Assessing Aortic Stenosis Grading
TABLE 3-2 LIMITATIONS AND IMPLICATIONS IN ASSESSING AORTIC STENOSIS
| Limitations | Implications | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | ||
| AS jet velocity (CW Doppler) | ||
| AS pressure gradient (CW Doppler) | ||
| Velocity ratio (VR = VLVOT/VAV) | ||
| AVA planimetry Anatomic AVA | ||
| AVA continuity Measures EOA |
AS, aortic stenosis; AV, aortic valve; AVA, aortic valve area; CO, cardiac output; CW, continuous wave; EOA, effective orifice area; LV, left ventricular; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; LVOT, left ventricular outflow tract; MR, mitral regurgitation; SVR, systemic vascular resistance.
From Baumgartner H, Hung J, Bermejo J, et al. Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22:1-23.
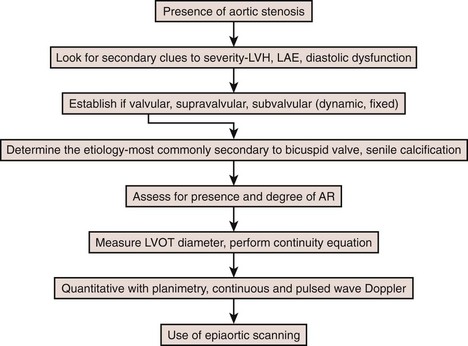
Step 5a: No Discrepancies in Aortic Stenosis Quantification
Aortic Regurgitation
Key Points