Echocardiography
Two and three-dimensional echocardiography provides the image (transesophageal echocardiography or TEE is better than transthoracic echocardiography or TTE) to measure the aortic valve area and to evaluate the extent of leaflet calcification.
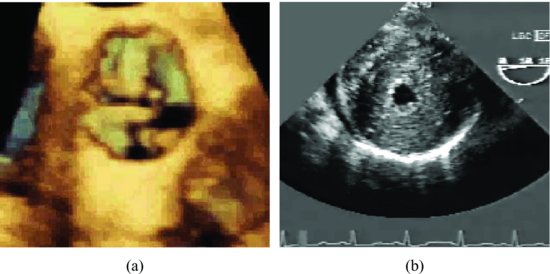
Other findings on the echocardiogram that may be helpful in the assessment of severity include patterns of leaflet motion; when leaflets move together in a “dome-like” pattern, the possibility of significant obstruction (or bicuspid valve) is increased. In significant stenosis cases, poststenotic dilatation is usually present. The varying degrees of concentric left ventricle hypertrophy (LVH) may present. The examples of cases with severe aortic stenosis are shown in Figure 7.2 and Videoclip 7.2.
Figure 7.2 Three-dimensional image shows thickened and stenotic aortic valve (a). Transesophageal echocardiographic image shows a hypertrophied left ventricle due to severe aortic stenosis (b).
Doppler echocardiography
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


