Amputation and Rehabilitation
Definition
The intentional surgical removal of a limb (almost always part of the foot or leg in the vascular context).
Epidemiology
Eighty per cent in the UK due to vascular disease, 25% of which are diabetic.
Indications
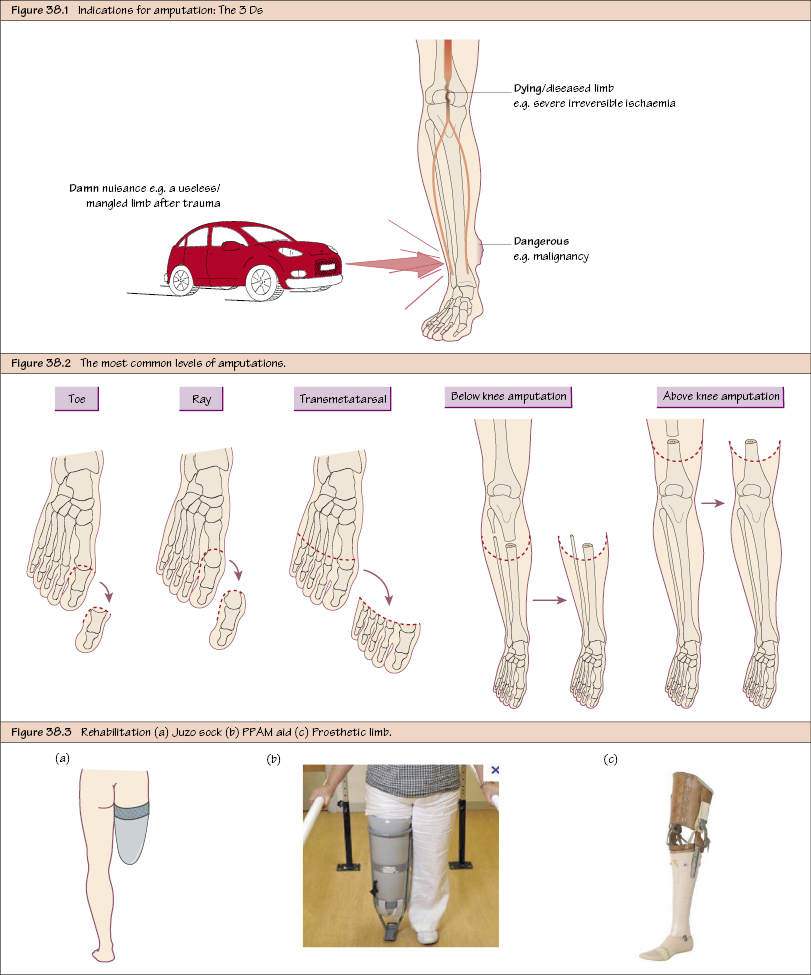
The 3 Ds:.
- Dying/Diseased limb (e.g. irreversible ischaemia).
- Dangerous (e.g. malignancy or severe foot sepsis).
- Damn nuisance/useless (e.g. severe malformation or following trauma).
Levels of Amputation
Proximal to Distal:
- Toe/digit (through proximal phalanx or metatarsophalangeal joint [MTPJ]).
- Ray (through one metatarsal).
- Transmetatarsal (through all transmetatarsals).
- Chopart’s (midtarsal, very rare now).
- Syme’s (through ankle joint, very rare now).
- BK (transtibial, either skew flap or long posterior flap).
- Through knee.
- Gritti Stokes (a particular technique of through-knee amputation).
- AK (transfemoral).
- Hip disarticulation (rare, more for malignancy).
Choosing the Level of Amputation
Only gold members can continue reading.
Log In or
Register to continue
Related

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel