CASE 52 Percutaneous Repair of Atrial Septal Defect
Case presentation
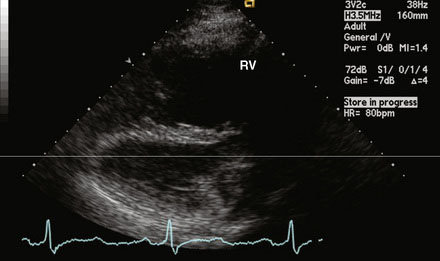
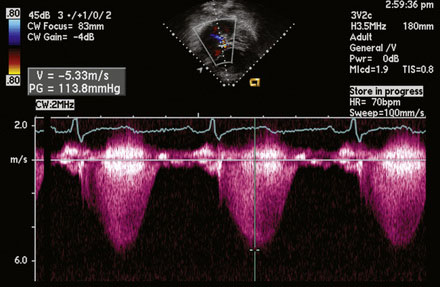
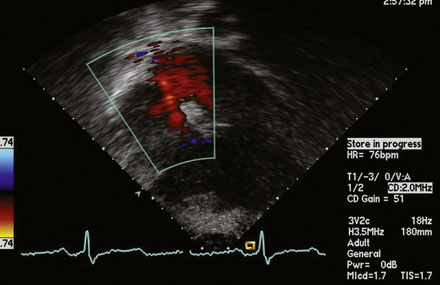
A 12-lead surface electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus rhythm with right axis deviation and a narrow RSR’ in V1, consistent with right ventricular enlargement. Transthoracic echocardiography demonstrated a markedly dilated right ventricle (Figure 52-1 and Video 52-1) and a tricuspid regurgitant Doppler signal consistent with severe pulmonary hypertension (Figure 52-2). Subcostal imaging demonstrated an atrial septal defect with significant left-to-right shunt across the atrial septum (Figure 52-3 and Video 52-2). There was normal left ventricular size and systolic function. She was referred for percutaneous closure of the atrial septal defect.
Cardiac catheterization
The procedure was performed using conscious sedation. Vascular access initially consisted of a 6 French sheath in the right femoral artery and both 8 and 11 French sheaths in the right femoral vein. The patient received 4000 U of unfractionated heparin intravenously along with 1 g of cefazolin. A 10.5 French intracardiac echocardiography catheter was then inserted through the 11 French sheath and advanced to the right atrium, allowing imaging and sizing of the atrial septal defect as well as confirming normal pulmonary venous return to the left atrium (Figure 52-4
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree