Chapter 5
Questions
- 81. The Doppler signal is consistent with:
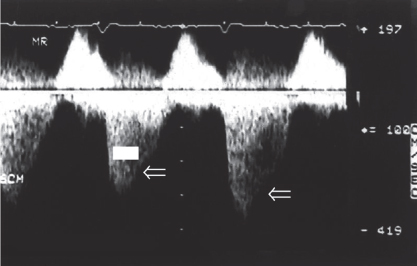
- A. Severe aortic regurgitation and moderate aortic stenosis
- B. Severe mitral stenosis
- C. Acute severe mitral regurgitation
- D. Ventricular septal defect
- 82. Pulse duration is affected by:
- A. Source of ultrasound
- B. B.Transmission medium
- C. Both
- D. Neither
- 83. The pulse repetition frequency (PRF) is affected by:
- A. Source of ultrasound
- B. Transmission medium
- C. Both
- D. Neither
- 84. What happens to the PRF when imaging depth is increased?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. C.Does not change
- D. Effect is variable
- 85. By increasing the PRF, the axial resolution:
- A. A.Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Does not change
- 86. Imaging at depth affects:
- A. Axial resolution
- B. Lateral resolution
- C. Neither
- D. Both
- 87. Reducing the transducer footprint will affect:
- A. Lateral resolution
- B. Temporal resolution
- C. Axial resolution
- D. None of the above
- 88. Increasing the transmit power will:
- A. Decrease sensitivity
- B. Increase lateral resolution
- C. Increase penetration
- D. None of the above
- 89. Acoustic impedance equals (rayls):
- A. Density in kg/m3 × speed of sound in m/s
- B. Density in kg/m3 × transducer frequency in MHz
- C. Depth in meters × transducer frequency in MHz
- D. None of the above
- 90. Reflection of sound at an interface is affected by:
- A. Specific acoustic impedance
- B. Transducer frequency
- C. Depth
- D. None of the above
- 91. The most common cause of coronary sinus dilatation is:
- A. Heart failure
- B. Persistent left superior vena cava
- C. Atrial septal defect
- D. None of the above
- 92. The following data were obtained from a 72-year-old man with a calcified aortic valve: left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) velocity (V1) 0.8 m/s, transaortic velocity (V2) 4 m/s, LVOT diameter 2 cm. The calculated aortic valve area (AVA) is:
- A. 0.4 cm2
- B. 0.6 cm2
- C. 0.8 cm2
- D. 1 cm2
- 93. The continuity equation is an example of:
- A. Law of conservation of mass
- B. Law of conservation of energy
- C. Law of conservation of momentum
- D. None of the above
- 94. The most practical value for the development of perfluorocarbon bubbles was to improve:
- A. Contrast on the right side
- B. Stable passage through the transpulmonary bed to improve contrast on the left side
- C. Improve contrast visualization in the hepatic bed
- D. None of the above

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- A. Severe aortic regurgitation and moderate aortic stenosis

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


