CASE 4 Coronary Aneurysm
Cardiac catheterization
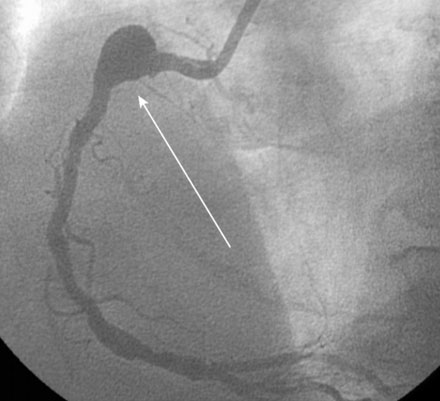
Ventriculography revealed normal left ventricular function. The left coronary artery was angiographically normal. Right coronary angiography, however, demonstrated a large focal aneurysm of the proximal coronary artery, measuring nearly 10 mm in diameter, with a moderate stenosis in the midsegment of the vessel (Figure 4-1 and Videos 4-1, 4-2).
Following the diagnostic cardiac catheterization, the various treatment options were discussed in detail, including medical therapy, surgery, and percutaneous treatment using a covered stent. After much discussion, the patient chose to undergo treatment with a covered stent. After loading with 300 mg of clopidogrel, the patient returned to the cardiac catheterization laboratory for this procedure. Bivalirudin was used as the procedural anticoagulant. The operator engaged the right coronary artery with an 8 French right Judkins guide and positioned an extra-support 0.014” guidewire distally. A 5.0 mm diameter, 22 mm long polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) covered stent (Atrium iCast, Atrium Medical Corporation) was centered over the aneurysm (Figure 4-2) and deployed. The angiogram obtained after stent deployment showed a small residual leak into the aneurysm sac at the proximal end of the stent (Figure 4-3 and Video 4-3). The operator proceeded with placement of a 4.0 mm diameter by 15 mm long bare-metal stent at the moderate stenosis in the midsegment of the vessel (Figure 4-4), resulting in an excellent angiographic result at this site; however, there remained a small leak into the aneurysm (Video 4-4). A second covered stent (5.0 mm diameter by 16 mm long) was used to cover this small residual leak (Figure 4-5
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree