Chapter 21
Questions
- 401. This patient is likely to have:
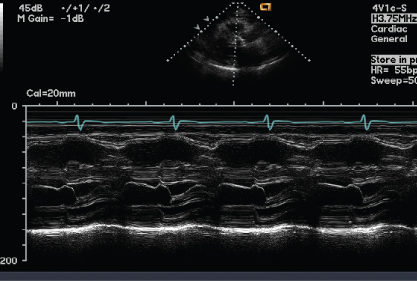
- A. Mitral valve prolapse
- B. Elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
- C. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- D. Severe aortic regurgitation
- 402. The mitral valve motion in this patient suggests:
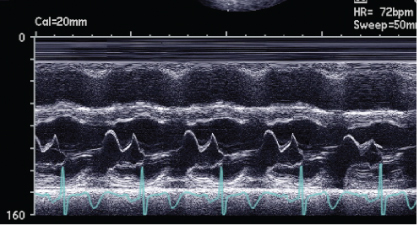
- A. Atrial fibrillation
- B. Elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
- C. Mitral valve prolapse
- D. Severe aortic regurgitation
- B. Elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
- 403. The aortic valve m-mode is suggestive of:
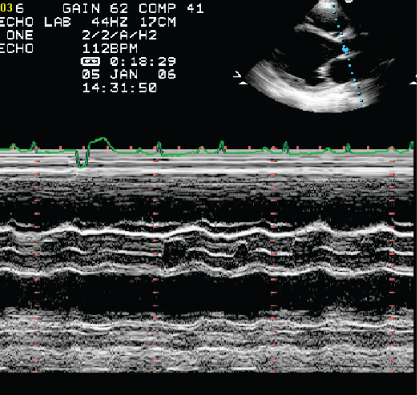
- A. Aortic stenosis
- B. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- C. Congestive heart failure
- D. Hypertension
- 404. Flow in abdominal aorta in this patient is indicative of:
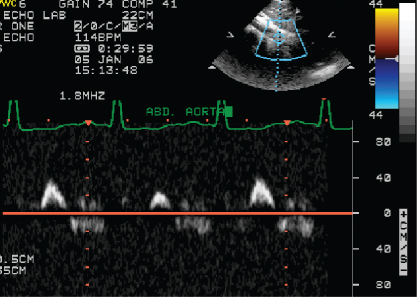
- A. Systolic heart failure
- B. Severe coarctation of aorta
- C. Severe aortic regurgitation
- D. Large patent ductus arteriosis
- B. Severe coarctation of aorta
- 405. The continuous wave Doppler signal is suggestive of:
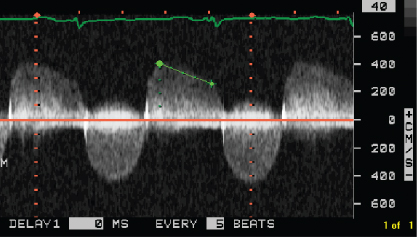
- A. Severe mixed aortic valve disease
- B. Mixed pulmonary valve disease
- C. Mixed mitral valve disease
- D. Mitral and aortic regurgitation
- 406. This patient is likely to have:
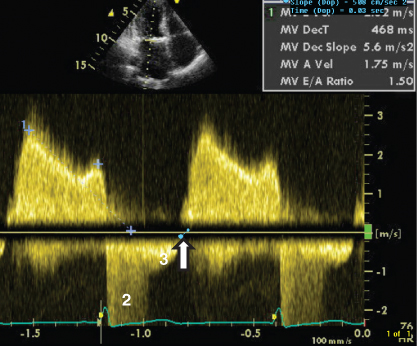
- A. Mild aortic regurgitation
- B. Mitral stenosis with high LA pressure
- C. Acute severe aortic regurgitation
- D. Severe mitral regurgitation
- 407. This patient has mitral stenosis with:
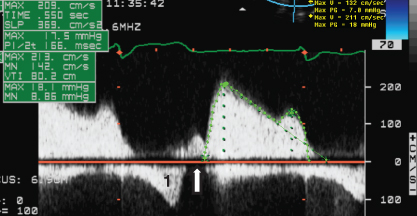
- A. High LA pressure
- B. Hyperdynamic LV
- C. Severe LV systolic dysfunction
- D. Mitral regurgitation
- 408. The continuous wave Doppler signal is suggestive of:
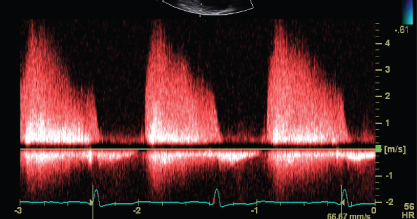
- A. Mild mitral stenosis
- B. Severe mitral stenosis
- C. Mild aortic regurgitation
- D. Severe aortic regurgitation
- 409. The continuous wave Doppler signal is suggestive of:
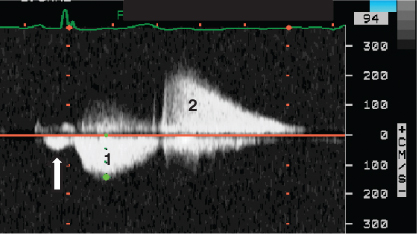
- A. Severe aortic regurgitation
- B. Mitral stenosis
- C. Pulmonary hypertension
- D. Severe pulmonary regurgitation
- 410. This patient has:
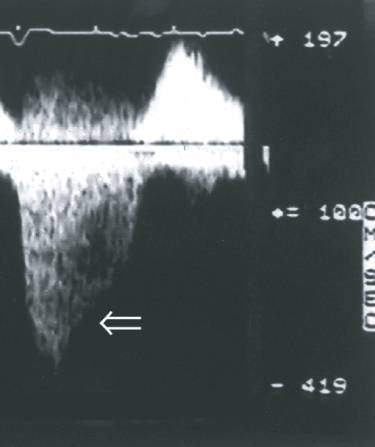
- A. Mild to moderate aortic stenosis
- B. Mild mitral regurgitation
- C. Acute severe mitral regurgitation
- D. VSD with Pulmonary hypertension
- 411. The cause of systolic murmur in this patient is likely to be:
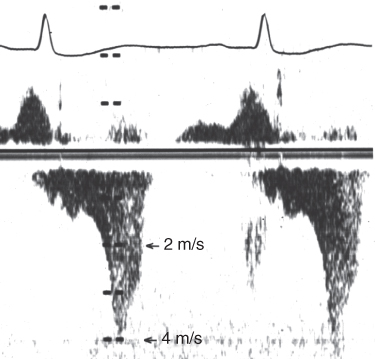
- A. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- B. Valvular aortic stenosis
- C. Mitral valve prolapse
- D. VSD
- 412. This CW signal in a 22-year-old woman with a history of heart surgery during infancy is indicative of:
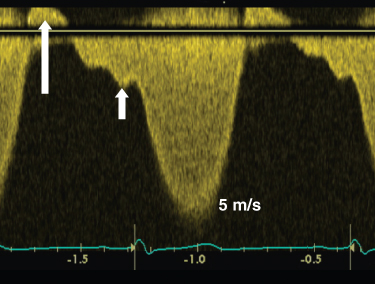
- A. Severe aortic stenosis
- B. Severe pulmonary stenosis
- C. Severe pulmonary stenosis and regurgitation
- D. Severe pulmonary hypertension
- 413. This patient has:
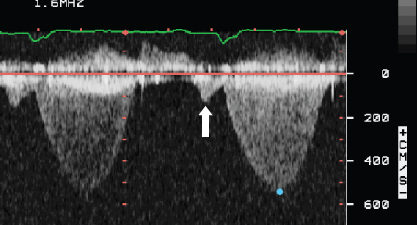
- A. Severe pulmonary stenosis
- B. Normal pulmonary artery pressure
- C. Both are true
- D. Neither is true
- 414. The signal indicated by the arrow is produced by:
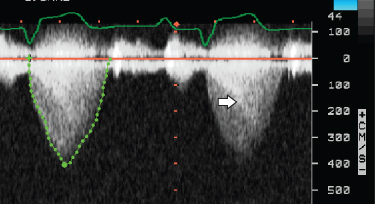
- A. Pulmonary valvular stenois
- B. Dynamic subvalvular PS on top of valvular PS
- C. Mitral regurgitation
- D. VSD
- B. Dynamic subvalvular PS on top of valvular PS
- 415. This signal was obtained from:
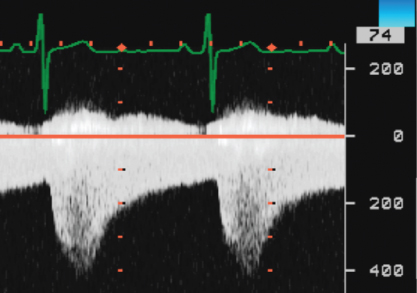
- A. Apical window
- B. Parasternal window
- C. Suprasternal window
- D. Subcostal window
- 416. This patient has:
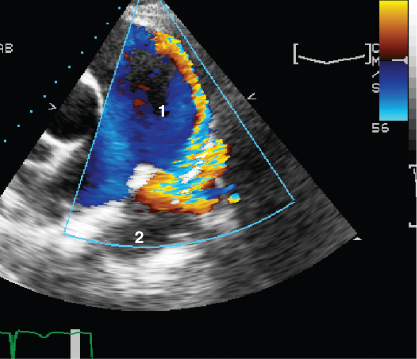
- A. Pulmonary artery branch stenosis
- B. Pulmonary regurgitation
- C. Patent ductus arteriosus
- D. None of the above
- 417. This CW signal is indicative of:
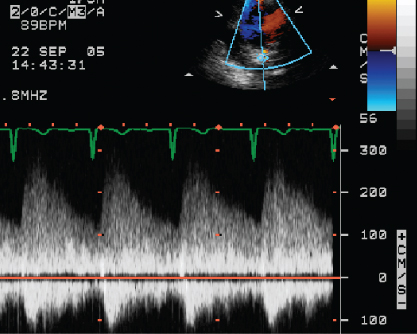
- A. Severe aortic regurgitation
- B. Patent ductus arteriosus
- C. Coarctation of the aorta
- D. ASD flow
- 418. The flow obtained on TEE from descending thoracic aorta is indicative of:
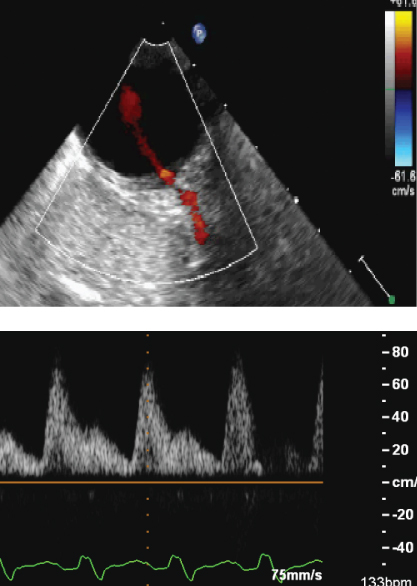
- A. Aortic coactation
- B. PDA
- C. Normal flow in intercostal artery
- D. Severe aortic regurgitation
- B. PDA

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- A. Mitral valve prolapse

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


