Chapter 18
Questions
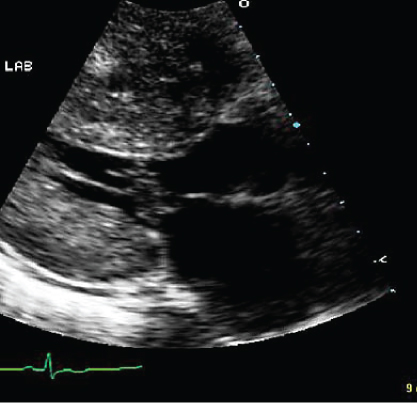
- 341. This continuous wave Doppler signal is indicative of:
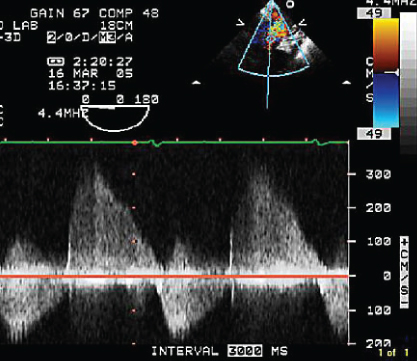
- A. Acute severe aortic regurgitation (AR)
- B. Chronic compensated AR
- C. Severe aortic stenosis (AS)
- D. Severe mixed mitral valve disease
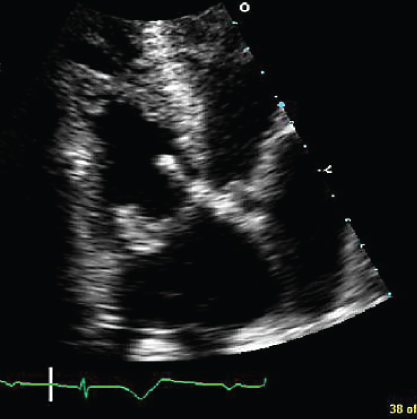
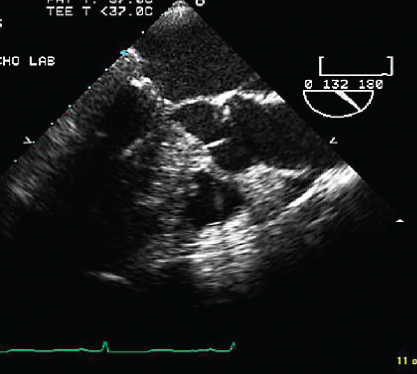
- 342. This transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) image is suggestive of:
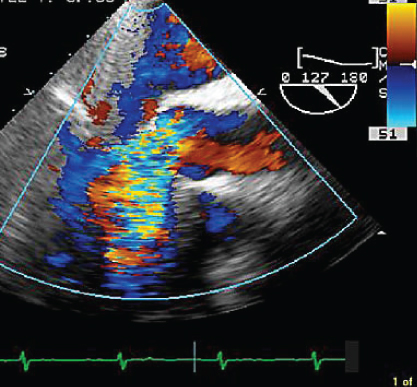
- A. Severe AR
- B. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
- C. Subaortic membranous aortic stenosis
- D. None of the above
- B. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
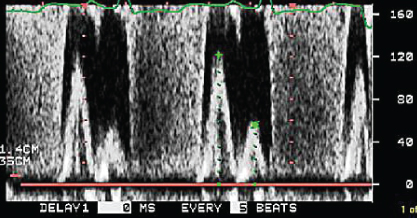
- 343. This pulse wave Doppler flow signal in the descending thoracic aorta on a TEE is indicative of:
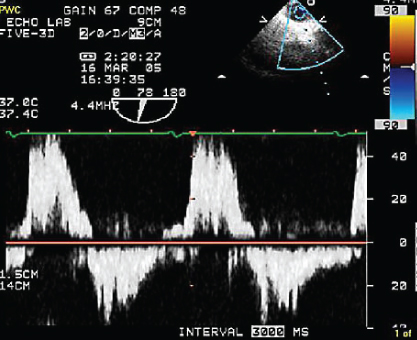
- A. Coarctation of the aorta
- B. Middle aortic syndrome
- C. Severe AR
- D. HOCM
- 344. What procedure did this patient undergo?
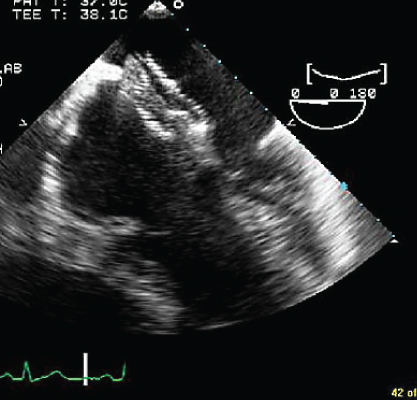
- A. Mitral valve replacement
- B. Atrial septal defect (ASD) closure with an Amplatzer device
- C. Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure with cardioseal device
- D. Closure of ASD with a pericardial patch
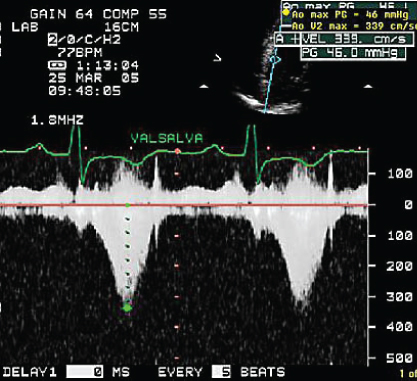
- 345. This patient is likely to have:
- A. Systolic murmur accentuated by Valsalva maneuver
- B. Early peaking systolic murmur
- C. Early diastolic murmur heard in sitting position at end expiration
- D. A middiastolic murmur best heard with the bell in left lateral position
- B. Early peaking systolic murmur
- 346. This signal shown here is likely to be caused by:
- A. HOCM
- B. Critical valvular aortic stenosis
- C. Acute mitral regurgitation (MR)
- D. None of the above
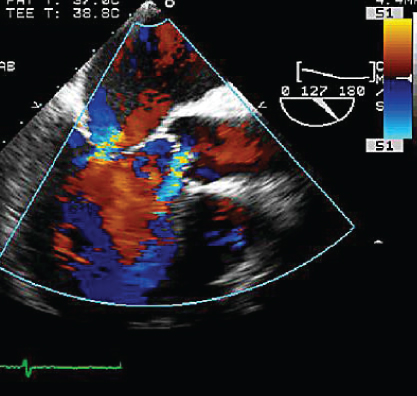
- 347. The image shown here is suggestive of:
- A. Bioprosthetic tricuspid valve
- B. Carcinoid valvulopathy of the tricuspid valve
- C. Tricuspid annuloplasty ring
- D. Large tricuspid vegetation
- B. Carcinoid valvulopathy of the tricuspid valve
- 348. This 65-year-old patient with MR is likely to have:
- A. An opening snap
- B. Third heart sound
- C. Fourth heart sound
- D. Summation gallop
- 349. The CW Doppler signal is consistent with:
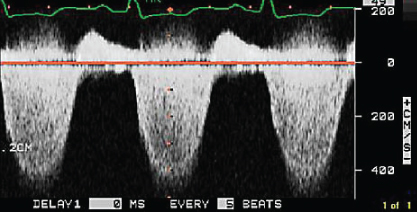
- A. Critical AS
- B. Severe MR
- C. Maladie de Roger
- D. None of the above
- 350. This tricuspid regurgitation (TR) signal was obtained from TEE. The clinically estimated right atrial (RA) pressure in this patient was 20 mmHg and there is no pulmonary stenosis. The pulmonary artery (PA) systolic pressure in this patient would be:
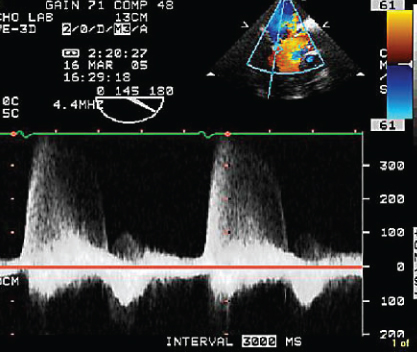
- A. 30 mmHg
- B. 50 mmHg
- C. 80 mmHg
- D. Cannot be calculated
- 351. This patient is likely to have:
- A. Acute severe AR
- B. Mild AR
- C. Mitral stenosis
- D. None of the above
- 352. This transmitral flow is obtained from the esophageal transducer location from a patient with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and acute hemodynamic decompensation. Patient is in sinus rhythm. The most likely cause of his decompensation is:
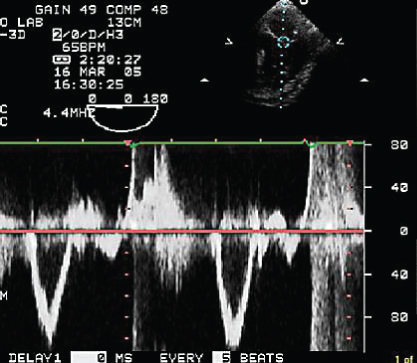
- A. Acute MR
- B. Acute AR
- C. Rupture of the ventricular septum
- D. None of the above
- 353. The cause of this patient’s multiple bilateral lung abscesses is:
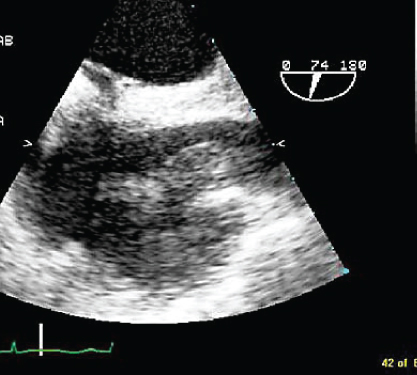
- A. Vegetation in superior vena cava (SVC)
- B. Tricuspid endocarditis
- C. Probable immune deficiency; no vegetation seen on image shown
- D. None of the above
- 354. The cause of heart failure in this 30-year-old man is likely to be:
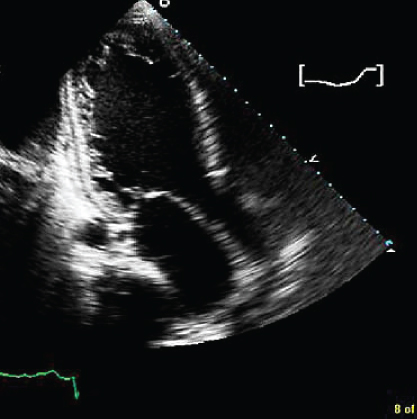
- A. Noncompaction of the left ventricle (LV)
- B. Hemochromatosis
- C. Cardiac amyloid
- D. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- 355. The structure indicated by the arrow is:
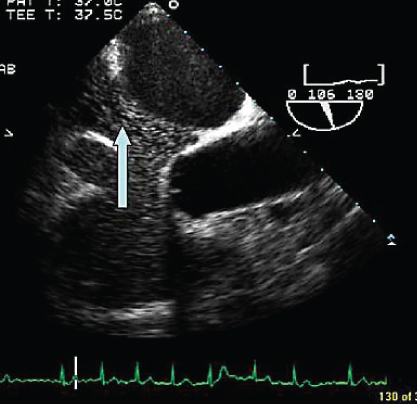
- A. Inferior vena cava (IVC)–RA junction
- B. Superior vena cava
- C. Anomalously draining right upper pulmonary vein
- D. Atrial septal defect
- 356. The MR flow rate in this patient (PISA radius of 0.9 cm, aliasing velocity of 38 cm/s) is approximately:
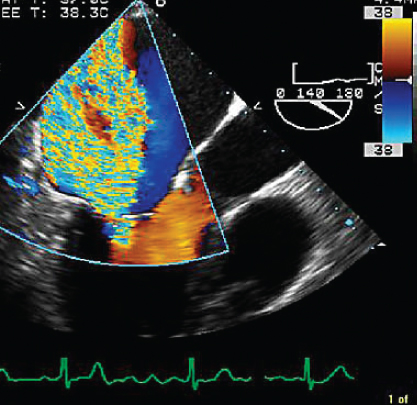
- A. 200 cc/s
- B. 200 cc/min
- C. 100 cc/min
- D. 100 cc/s
- 357. The patient shown is likely to have:

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- A. Acute severe aortic regurgitation (AR)

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


