Chapter 17
Questions
- 321. The cause of dyspnea in this patient is likely to be due to:
- A. Left heart failure
- B. Primary pulmonary hypertension
- C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
- D. None of the above
- 322. This is an end systolic frame in a patient with shortness of breath. The most likely diagnosis is:
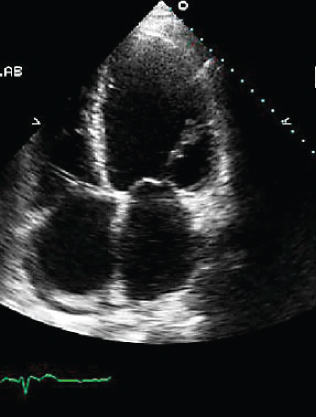
- A. Ebstein’s anomaly
- B. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- C. Atrial septal defect
- D. Dilated cardiomyopathy
- 323. The most likely mechanism of mitral regurgitation (MR) in this patient is:
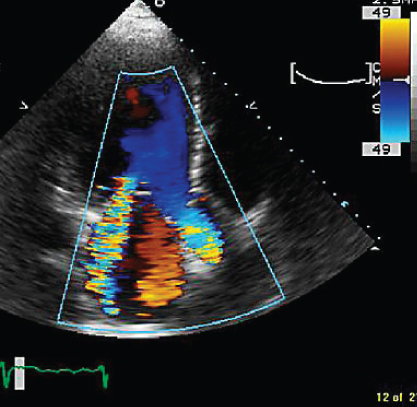
- A. P2 tethering
- B. P2 prolapse
- C. Bileaflet mitral valve prolapse
- D. None of the above
- 324. This 19-year-old patient was stabbed in the precordial area. Examination revealed a loud systolic murmur. The most likely cause of this murmur is:
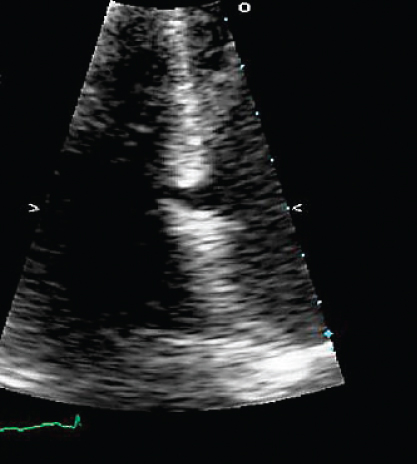
- A. Penetrating injury to the interventricular septum
- B. Mitral valve prolapse
- C. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
- D. None of the above
- 325. This transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) image is obtained from the upper esophagus, and the aortic arch is shown on the top. The arrow points to:
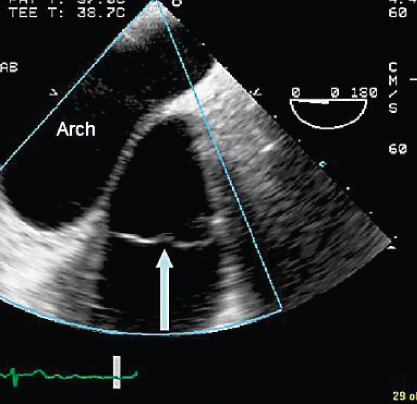
- A. Pulmonary valve
- B. Aortic valve
- C. Mitral valve
- D. Tricuspid valve
- B. Aortic valve
- 326. The structure indicated by the arrow is:
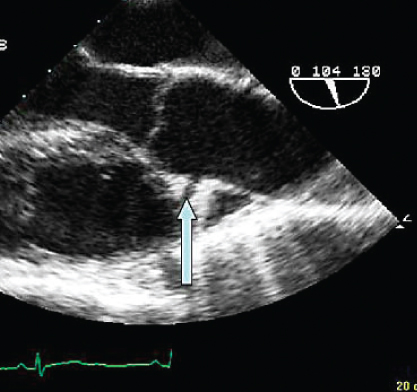
- A. Right coronary artery (RCA)
- B. Left coronary artery (LCA)
- C. Entry tear into dissection
- D. None of the above
- 327. This is a suprasternal image of the aortic arch, suggestive of:
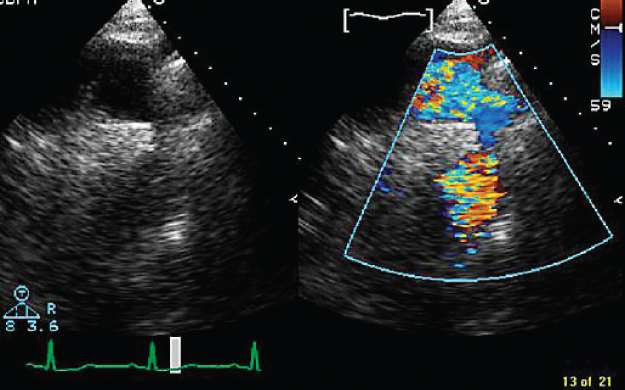
- A. Coarctation of the aorta
- B. Severe aortic regurgitation (AR)
- C. Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- D. None of the above
- B. Severe aortic regurgitation (AR)
- 328. In the accompanying image the structure indicated by the arrow is:
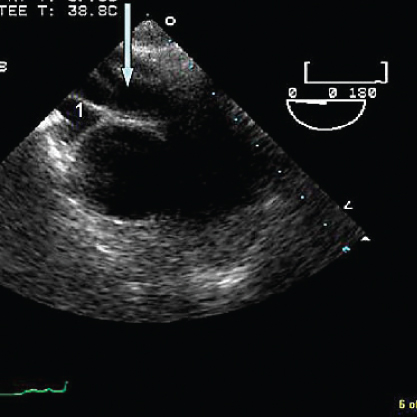
- A. Right pulmonary artery (RPA)
- B. Left atrium
- C. Aortic arch
- D. Right upper pulmonary vein
- 329. The structure denoted by the arrow is:
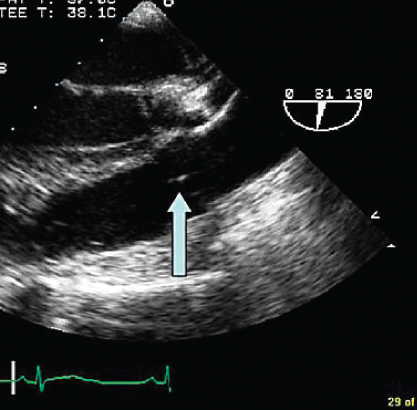
- A. An artifact
- B. Pulmonary valve
- C. Aortic valve
- D. Subpulmonic stenosis
- B. Pulmonary valve
- 330. What is the abnormality in the accompanying image?
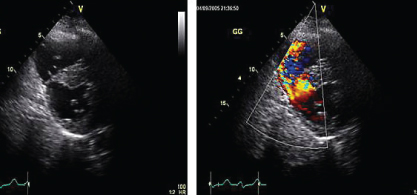
- A. Congenital muscular ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- B. Postinfarction posterior VSD
- C. Artifact of the normal posterior thinning at the valve plane
- D. Postmyectomy of HOCM
- 331. The abnormal finding in this image is:
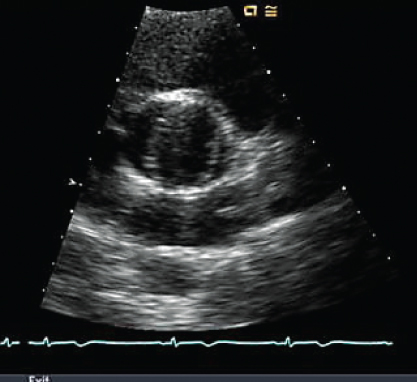
- A. Bicuspid aortic valve
- B. Aortic dissection flap
- C. Aortic aneurysm
- D. None of the above
- 332. Mitral regurgitation (MR) signal shown here is suggestive of:
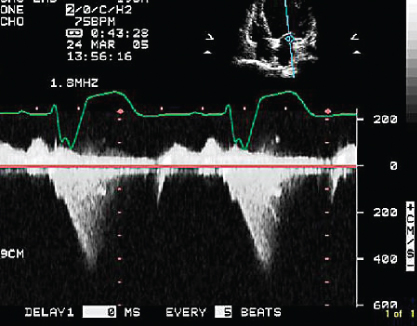
- A. Some diastolic MR in addition to systolic MR
- B. Markedly depressed left ventricular (LV) dp/dt
- C. Both
- D. Neither
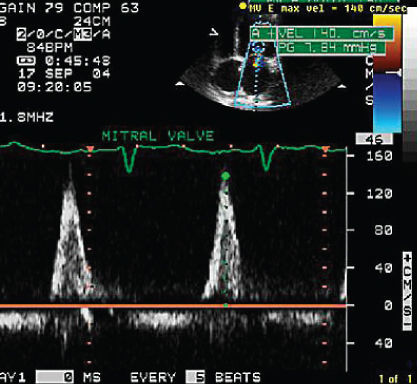
- 333. Mitral flow profile shown here is suggestive of:
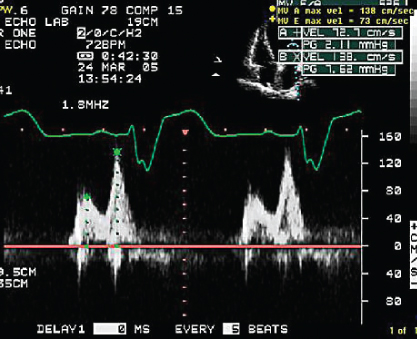
- A. Normal LV diastolic function
- B. Abnormal relaxation
- C. Pseudonormal pattern
- D. Restrictive pattern
- 334. This image shows:
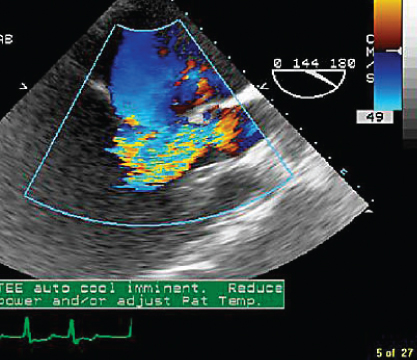
- A. Normal flow in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT)
- B. Subvalvular aortic stenosis (AS)
- C. Aortic regurgitation
- D. None of the above
- 335. This continuous wave Doppler signal is suggestive of:
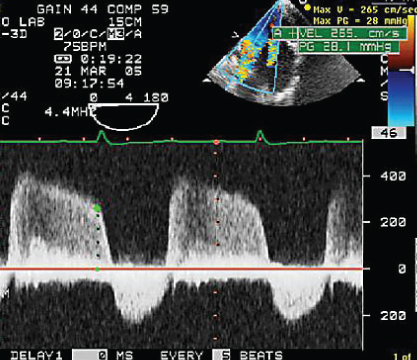
- A. AS and AR
- B. Mitral stenosis (MS) and MR
- C. VSD flow
- D. Aortic flow in a patient with coarctation
- 336. This continuous wave signal obtained from the midtransesophageal location is indicative of:
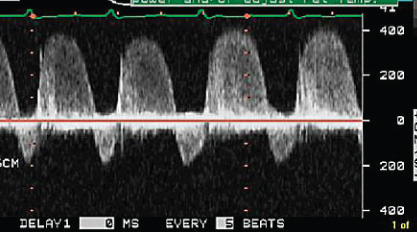
- A. AS and AR
- B. MS and MR
- C. VSD flow
- D. None of the above

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- A. Left heart failure

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


